Date created: Saturday, April 29, 2017 6:01:00 PM. Last modified: Wednesday, August 27, 2025 3:37:30 PM
UK Chamber Covers
Pictures of chamber covers that belong to various communications companies, taken around the UK. Some ducts contain fibre, some copper. Some are used exclusively for telecoms infrastructure and some for national and industrial infrastructure. Please send corrections to jwbensley [at] gmail (d0t) com. Click on pictures for a larger version.
If you haven't seen this presentation by Charlie Boisseau at UKNOF41, it's very good and explains the history behind many UK grid covers: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8I3XxniJdh8 (local slides mirror).
A great video on UK telecoms infrastructure that focuses on the sub-sea cables landing in Cornwall is available here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K_nnUbX7uuQ
ISPreview produced a guide to identifying different operators equipment here:
https://www.ispreview.co.uk/index.php/2019/12/identifying-bt-and-virgin-medias-uk-broadband-street-furniture-2019.html
This wiki is a great resource on the complex history of NTL / Telewest / VirginMedia: https://www.wikicorporates.org/wiki/Virgin_Media_Ltd
51 Degrees. 51 Degrees which was set-up in 2002, was originally a wholly owned subsidiary of London Electricity Group (LE Group). LE Group is an EDF company. 51 Degrees was a metro fibre and Ethernet provider around London, using London Electricities existing ducts and utility sites as PoP locations. 51 Degrees was purchased from EDF Energy by Interoute in 2007:
Atlantic Telecom. Originally founded in Scotland, Atlantic Telecom eventually went bankrupt in 2001/2002. In Manchester Atlantic built what later came to be called "The Loop" for the Manchester Commonwealth Games 2002. After Atlantic went under their fibre assets were domant for circa a decade. Gamma eventually bought The Loop and at the end of 2020 it was sold to EuNetworks. The Atlantic fibre outside of Manchester was eventually purchased by CityFibre.
Telcom are an ISP based in Manchester. Telcom lease capacity on The Loop to provide FTTP services around Manchester.
B4RN, B4SH, B4YS
B4RN (Broadband for the Rural North) started as a community run FTTH builder in rural North England in 2021. B4RN both expanded their own operation across the country, and inspired independent rural fire builders to use the same model (and even the same naming scheme). B4YS is an arm of B4RN called B4RN 4 Yealand, Silverdale & Storth. B4SH (Broadband for Surrey Hills) is not part of B4RN but based on the B4RN model.
BCP
Bournemouth, Christchurch, and Poole councils in the UK combined, and have their own fibre assets.
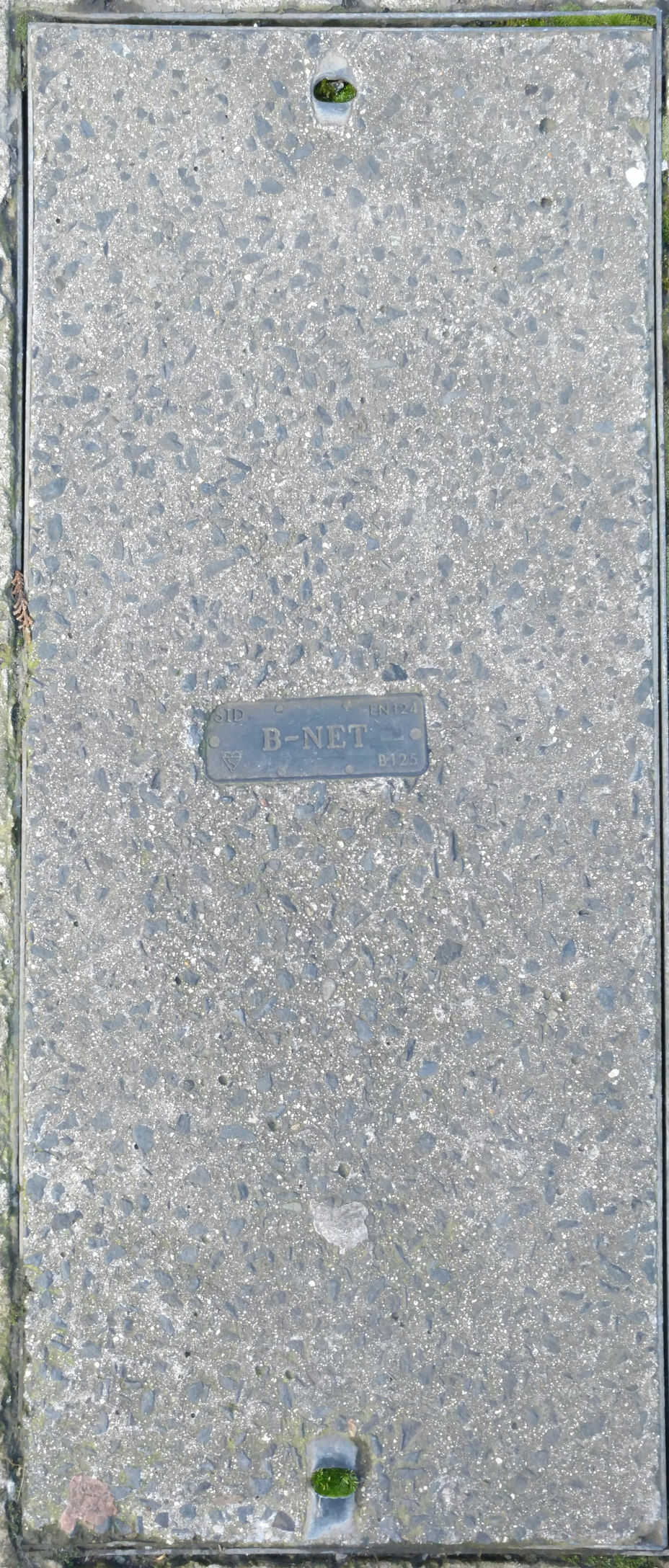
BET, BNET, Rediffusion:
Rediffusion was the trading name of Broadcast Relay Service Ltd, formed in 1928. In 1929 the company introduced its first cable radio service in Hull. In 1947 British Electric Traction (BET) acquired a substantial minority interest in Rediffusion. BET later acquired a controlling interest in 1967, and eventually 100% equity in 1983.
Rediffusion installed cable TV systems offering low-bandwidth cable TV and radio distribution systems, based on connecting homes with multiple twisted-pair cables. Each pair carried a single TV or radio channel.
The company also experimented with local cable operations: a local community station in Bristol ("Bristol Channel") from 1973 to 1976, and an optical fibre system in Hastings in 1976.
In the 1980s, Rediffusion's cable operations were left behind by the new generation of cable TV networks. BET began divesting and at the end of the 1980s the company was broken up with the cable network systems being sold to the Maxwell Communications.
The BNet (Bristol Network) is a 76km long ducting and fibre communications network, in a rough figure of eight, owned by BCC that has been around since 2000. It supports all the authority's requirements including telephony, data, the traffic network communications and CCTV. It was purchased from the Rediffusion divestment.
In October 2015 BCC approved a 20-year deal with two AltNets (Net Support UK and ITS Technology Group) to use the existing fibre and ducting network (and to extend it) for commercial offerings. The joint venture would trade as BNET Ultra Ltd and the network will be marketed under The Bristol Network brand.
On the 3rd September 1998 Net Support UK was born. In 2005, Connect Cardiff was created by the MD of NSUK. Connect Cardiff was rebranded in 2011 to become Spectrum Internet. Spectrum Internet (through NSUK) use the BNET to provide FTTP/H services.
brsk
brsk are an independent UK full fibre operator who started laying their own fibre in 2021 in West Yorkshire, and have since expanded to towns and cities across the UK.
Bogons are an ISP in the UK, started in 2000, who laying their own fibre. In 2017 they purchased the bulk of AB Internet’s network assets.
Bogons also support the Balquhidder Community Broadband (BCB) project which is deploying an FTTH network in Balquhidder:
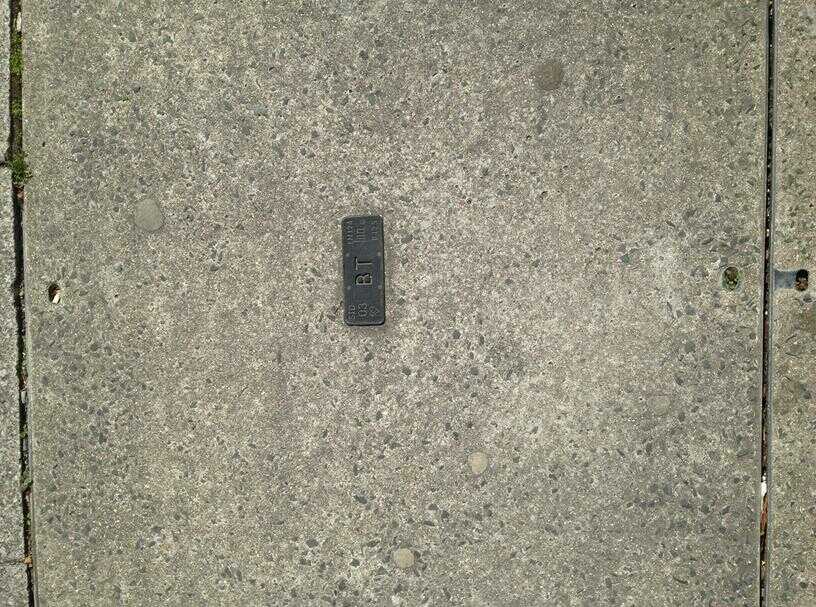
BT / British Telecom.
BT is the UK national incumbent formed out of the privatisation of the previously state owned Post Office Telecommunications network:
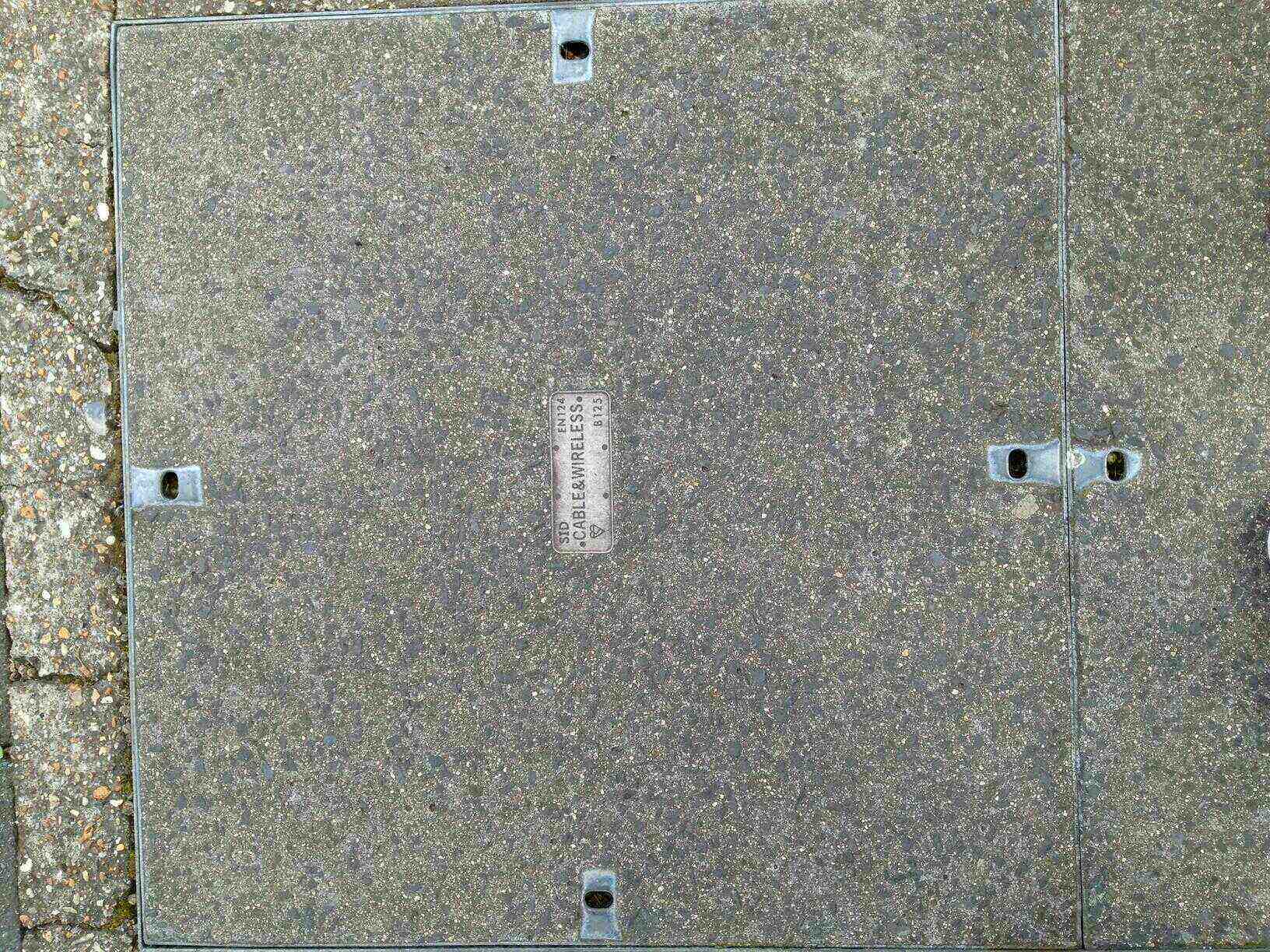
Cable and Wireless / C&W.
Cable and Wireless were acquired by Vodafone:
CableCom / Glide
In 2017 CableCom acquired AltNet WarwickNet.
CableCom rebranded to Glide in 2018.
In 2021 Glide acquired Concept Solutions People which was building it’s own fibre network.
In 2022 Glide acquired Velocity1 which was building it’s own fibre network.
Cambridge
Like many universities, Cambridge runs it's own network around the city
i3 / Redstone / Redcentric / Entanet / City Fibre
Originally i3 Group launched Fibrecity Holdings to build FTTH networks in 2009. Fibrecity Holdings also owned H2O Networks. Fibrecity Holdings' principal funder Total Asset Limited went into administration (a superb scandal ensued). In 2011 CityFibre Holdings took over the Fibrecity network and business, and H2O, and the original founder (i3 Group) went into administration. Since then CityFibre has grown to be one of the biggest FTTP/FTTH AltNets in the UK.
Redstone was a networking company with a metro fibre network in Cambridge, part of the Redstone Group (when was it formed?), which offered a range of managed IT services. In 2013 the network part was span out as Redcentric.
(this statement conflicts with the above statement?) Redcentric Plc was founded in 1997 and in 2000 started to build its own fibre metro-net around Cambridge (later it built metro-nets in other UK cities too). In 2016 Redcentric sold all their metro-nets to CityFibre.
Entanet was formed in 1996 and in 2017 Entanet was acquired by CityFibre.
In 2020 CityFibre bought TalkTalk's attempt at a wholesale fibre access network called FibreNation.
CNI / Cooperative Network Infrastructure
"Cooperative Network Infrastructure brings together public and private sector organisations to create and share new digital infrastructure in Tameside, Blackpool, Manchester and Sussex".
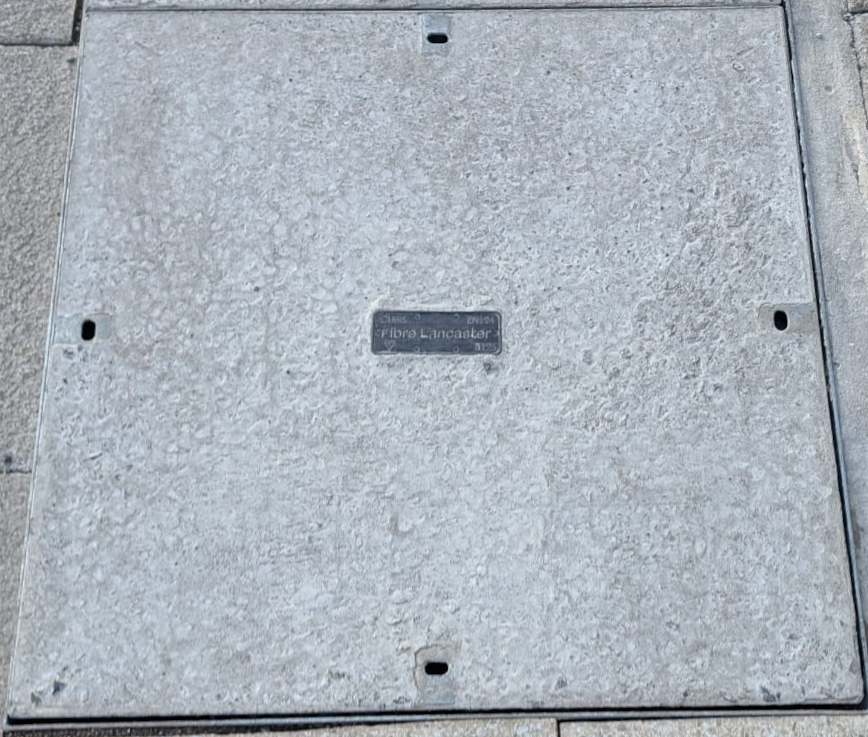
One such shared fibre network is the one installed and operated by TNP (The Network People) and B4RN (Broadband For Rural North) for Lancaster, Morecambe and Heysham.
Community Fibre
Community Fibre were founded in 2010 (?) and originally started providing high speed internet connectivity to properties in London using fixed wireless technologies. Later they started building out their own FTTH/FTTP network across London.
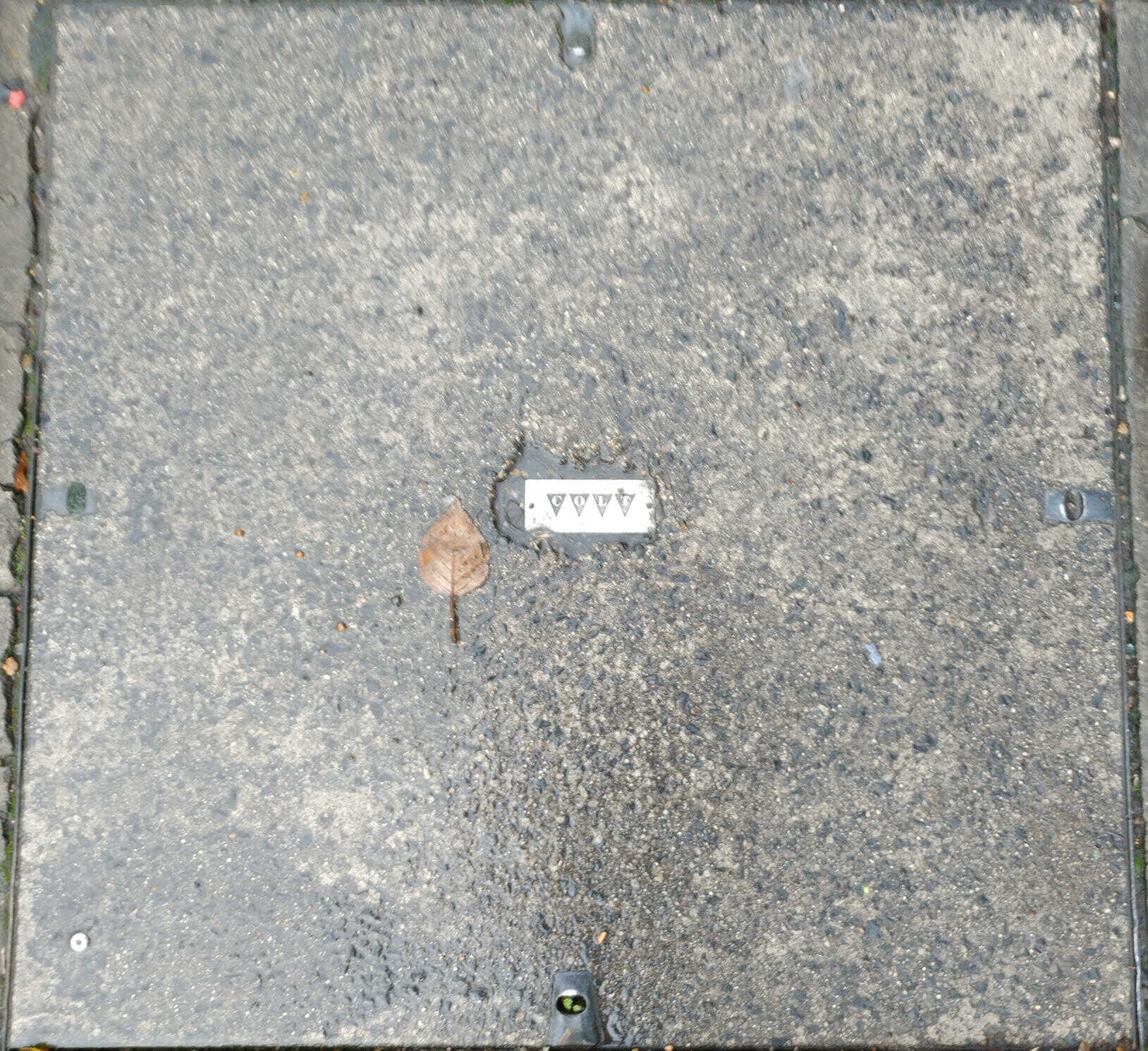
Colt
Colt (originally City Of London Telecommunications which later rebranded to Colt Technology Services as it expanded from it's original London centric scope to become pan-European).
Colt acquired MarketPrizm and KVH.
County Broadband Limited
CBL started as an FTTH operator building their own fibre network in the east of England (Cambridgeshire, Essex, Norfolk, Suffolk).
Truespeed started as an FTTH operator building their own fibre network in the west of England (Devon, Wiltshire, Somerset).
In August 2025 the two companies merged to form Truespeed Communications Group Ltd.
Photo provided by Trevor Cook.
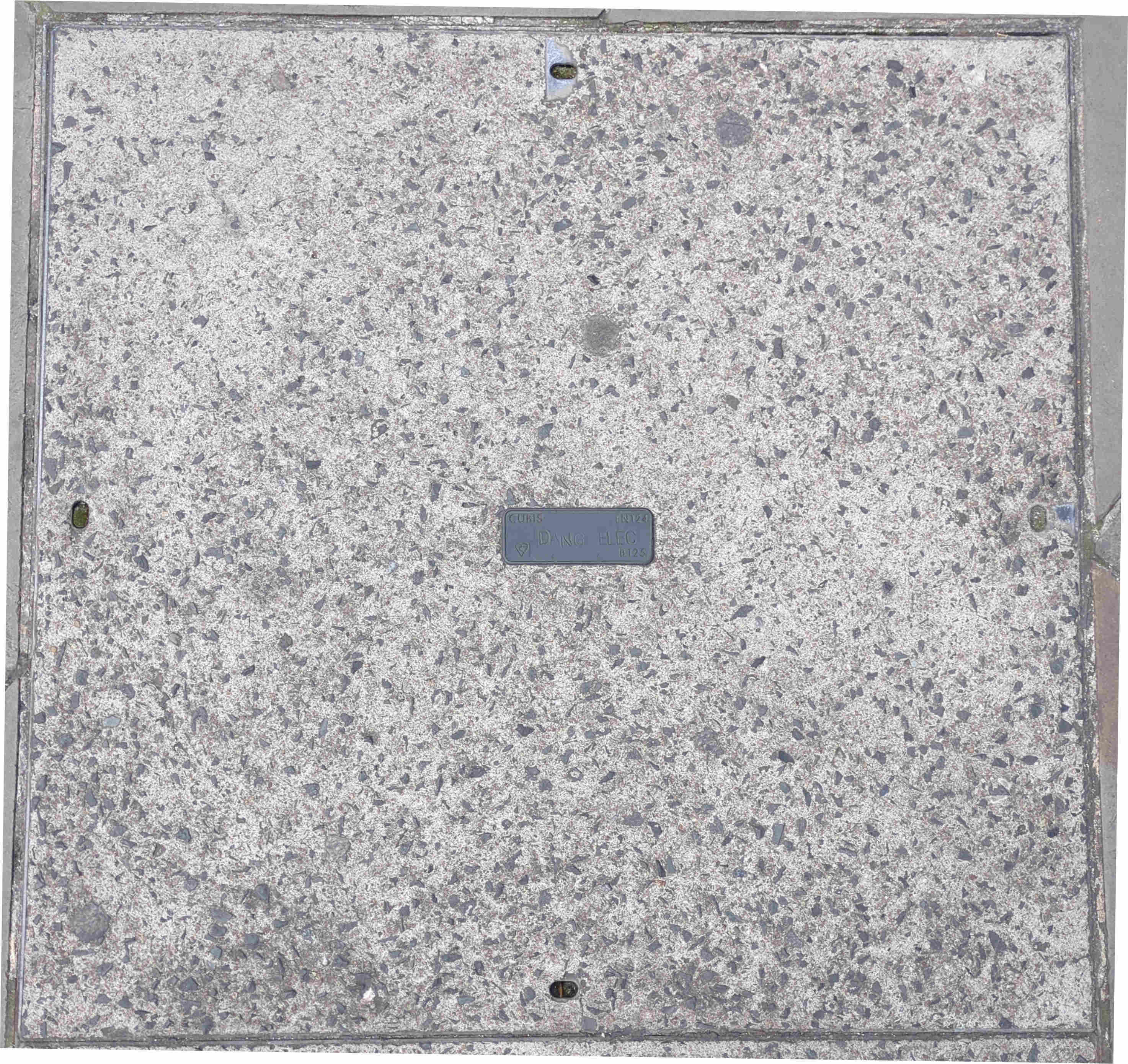
Dang Elec
? Seen in central London ?
ECOM
Ecom International Network is a trading name of Electronic Communities Ltd. Ecom Fibre is the FTTH/P product of Electronic Communities Ltd that operates across the UK county of Buckinghamshire:
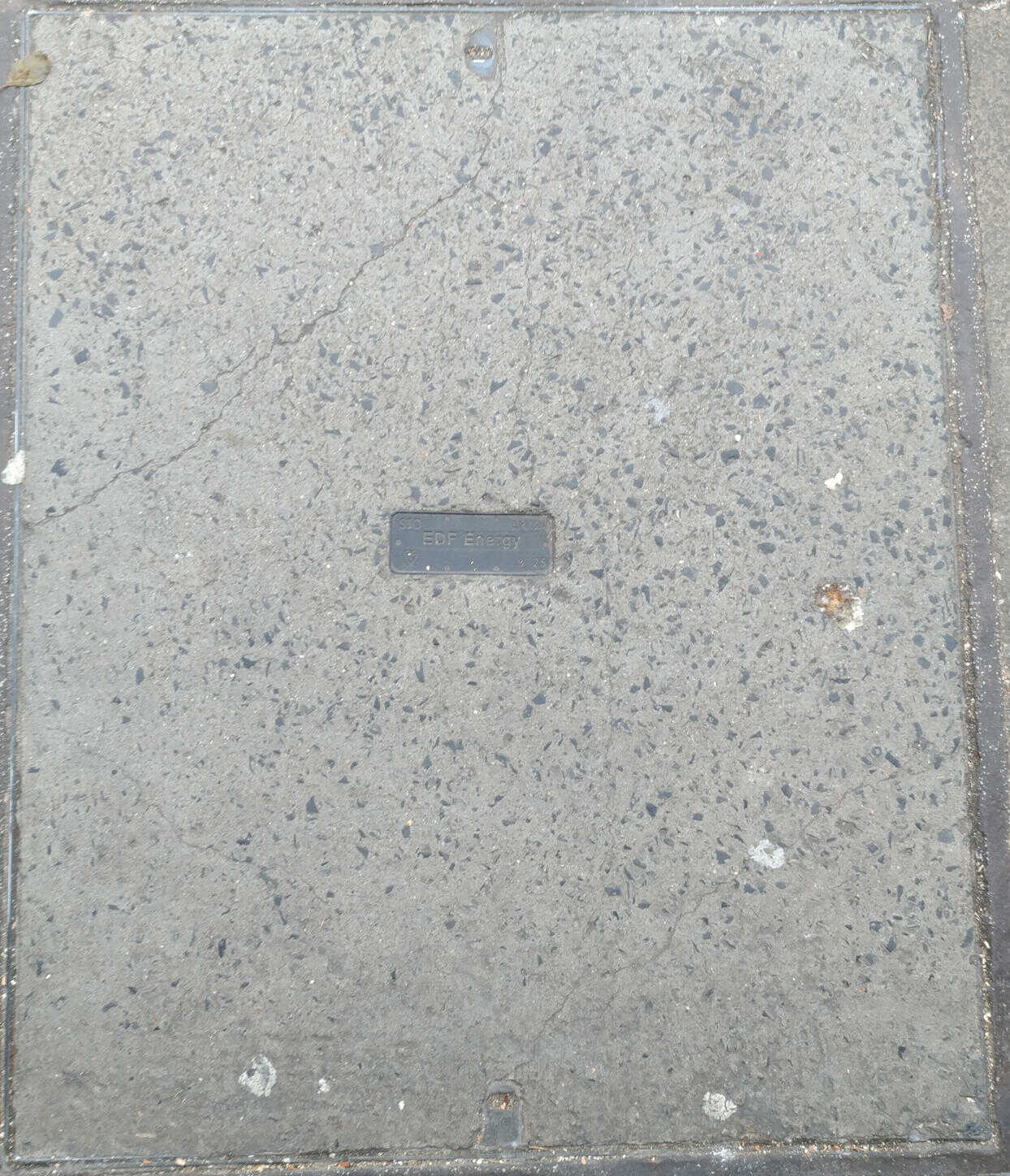
EDF Energy is the UK utility subsidiary of EDF (Électricité de France). It is common in the UK for utility companies to deploy communications infrastructure such as copper and fibre along their existing gas or water routes/ducts/tunnels/trenches. The London Electricity Board (LEB) trading as London Electricity PLC was founded in 1948 as a public sector utility company. It was privatised in 1990, in 1996 it was sold to Entergy and in 1998 sold to EDF:
Energis (originally Telecom Electric). Telecome Electric was a demerger from the UKs National Grid formed in 1991, "Its national optical fibre network was partially deployed via the overhead power transmission network of the grid". Telecome Electric later became Energis which was later acquired by Cable and Wireless, before C&W was acquired by Vodafone:
EuNetworks are a fibre and Ethernet/IP carrier covering most of western Europe founded in 2002:
Ex Tel Co
The Exchange Telegraph Company Limited (also known as Extel) was created in March 1872 specifically to distribute financial and business information. The Ex Tel network went through a series of M&As, one version of the company still exists (Extel Survey) but, the network is possibly defunct?
(Photo from https://manhole.co.il/)

Exa Infrastructure
Exa own and operate a pan European and North American terrestrial and sub-sea fibre network.
Exascale
Exascale started as a FTTH operator building their own fibre network in the West Midlands (Telford, Shropshire, and West Bromwich).
Photo provided by Thomas Bib.
Fibrus
Fibrus started in 2018. They are an FTTH/FTTP builder originally focused in Northern Ireland, they are expanging across England.
FullFibre are a UK FTTH ISP building their own fibre network across the UK to provide wholesale ISP connectivity (picture provided by Tom Brook):
G.Network Communications Ltd or "G.Networks" are a central London FTTH provider:
Gamma operate their own UK voice, data and mobile network:
Gas ?:
The BUUK Infrastructure Group owns GTC who are responsible for the construction and delivery of the fibre networks. BUUK also owns IFNL (Independent Fibre Network Limited) which runs the fibre network after GTC have delivered it:
Xara Networks / GX Networks / XO Networks / Pipex.
April 1997 - Internet Technology Group (ITG) announces the acquisition of Xara Networks Limited.
September 1997 - Xara Networks, a subsidiary of Internet Technology Group (ITG), relaunched as GX Networks.
January 2000 - GX Networks became part of Concentric Network.
September 2000 - Concentric Network merged with Nextlink to form XO Communications.
2001 - The UK arm of XO Europe was sold off to form Transigent Limited.
September 2002 - Zipcom plc acquires Transigent Limited (formerly XO Limited), the parent company of GX Networks in a deal worth approximately £10m.
October 2002 - Zipcom plc acquired the entire share capital of Transigent Limited the parent company of GX Networks.
March 2003 - Zipcom plc changed its name to GX Networks plc.
July 2003 - GX Networks acquires two more telecoms businesses XTML Limited ("XTML") and Compulink Information eXchange Limited ("CIX"), which were previously part of the Telenor Business Holdings UK Limited Group ("Telenor").
September 2003 - GX Networks buy Firstnet Ltd (owners of Liberty Broadband aka Tele2 UK).
October 2003 - GX Networks plc became Pipex Communications plc to maintain the PIPEX brand after a buy out for £55m.
May 2005 - Pipex Communications acquires Donhost.
2006 - Pipex Communications acquires Supanetwork, better known as SupaNames, for £2.2 million.
March 2008 - Due to Pipex Broadband being sold to Tiscali (now TalkTalk), the company known as Pipex Communications UK Ltd reverts to GX Networks Ltd.
Originally NTC (the National Telephone Company), then General Post Office / Post Office Telecommunications, they later became BT.
The GPO did at one point run a CATV service around inner London:
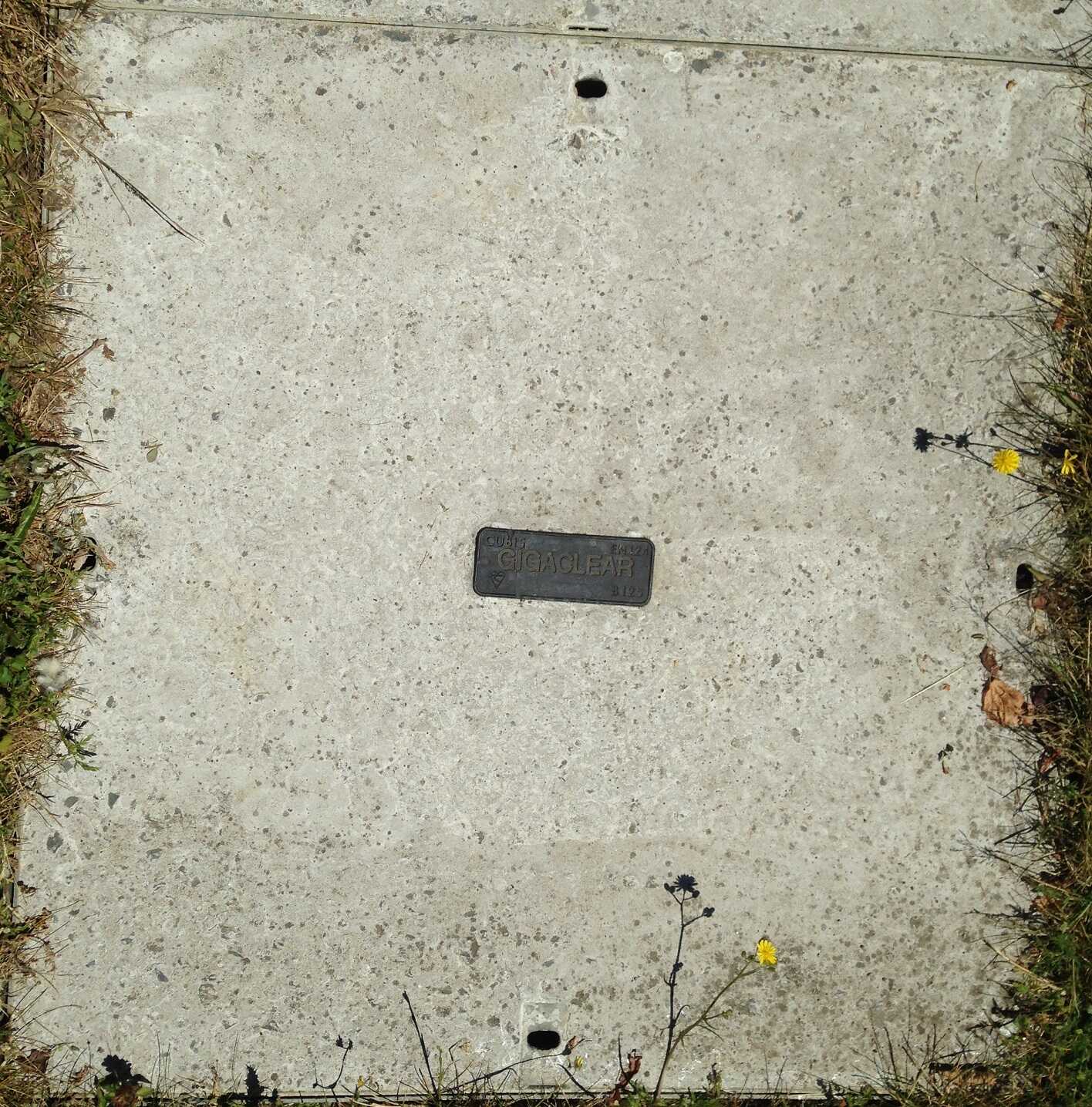
Gigaclear is a Fibre-to-the-Home/Premises provider which also owns Rutland Telecom. Gigaclear are a UK Alt Net who compete with BT Openreach in rural areas:
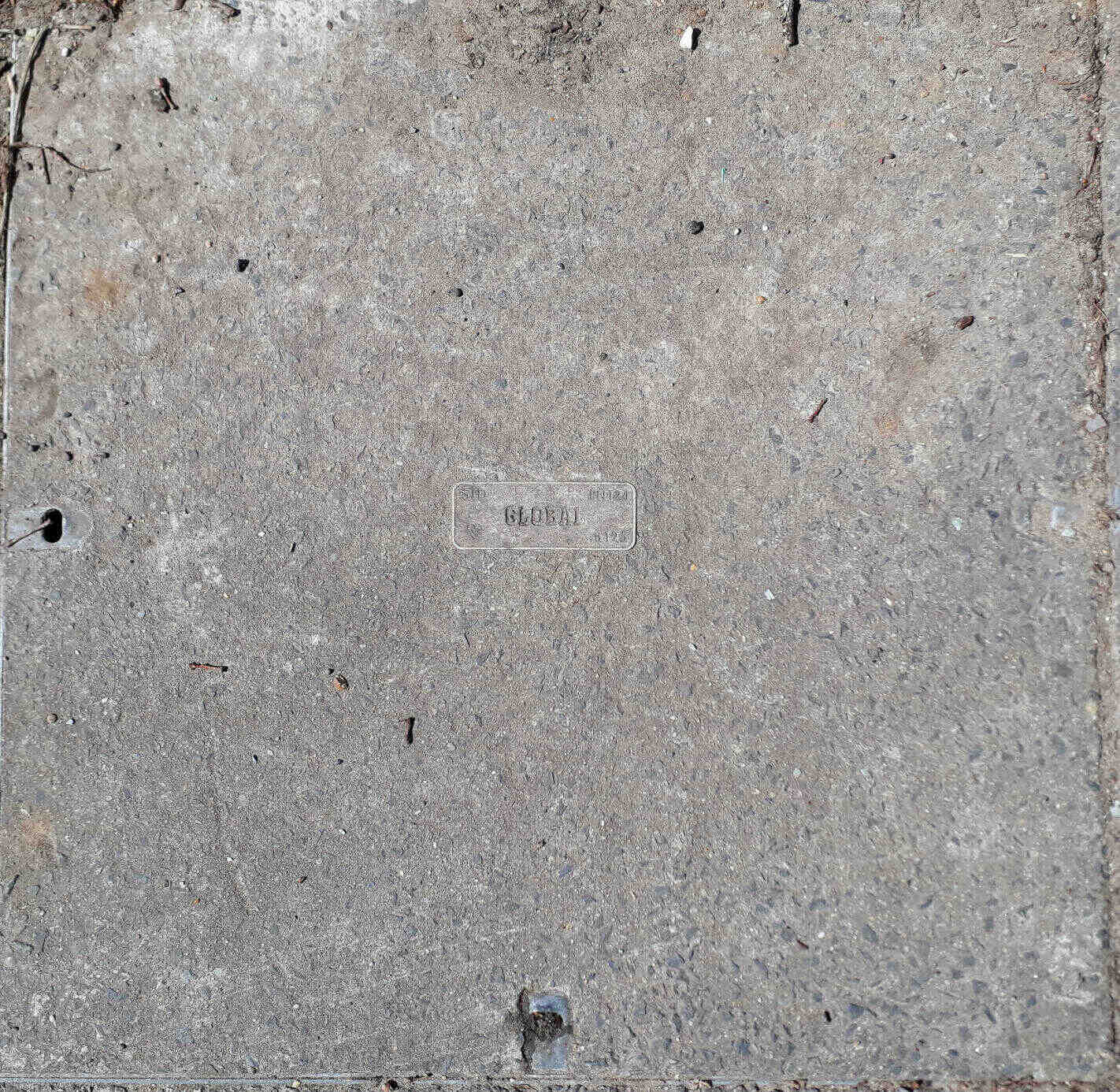
Global Cloud Xchange (FA-1):
Fibre-optic Link Around the Globe (FLAG) Telecom Group Ltd was formed in the mid 1990s and operated the FLAG fibre route.
Reliance Commnuications (RCOM) is/was (partial bankruptcy) part of the Reliance Group in India.
In 2003 Reliance acquired FLAG.
In 2007 Reliance acquired Yipes.
In 2008 Reliance acquired Vanco.
In 2008 Reliance renamed FLAG as Reliance Globalcom Limited (RGL)
In 2011 Reliance set up the Hawk cable system.
In 2014 Reliance Globalcom Limited (RGL) rebranded as Global Cloud Xchange (GCX). Global Cloud Xchange was formed as part of the rebranding of FLAG Telecom Group Limited, Reliance Vanco Group Limited and Yipes Holdings, Inc.
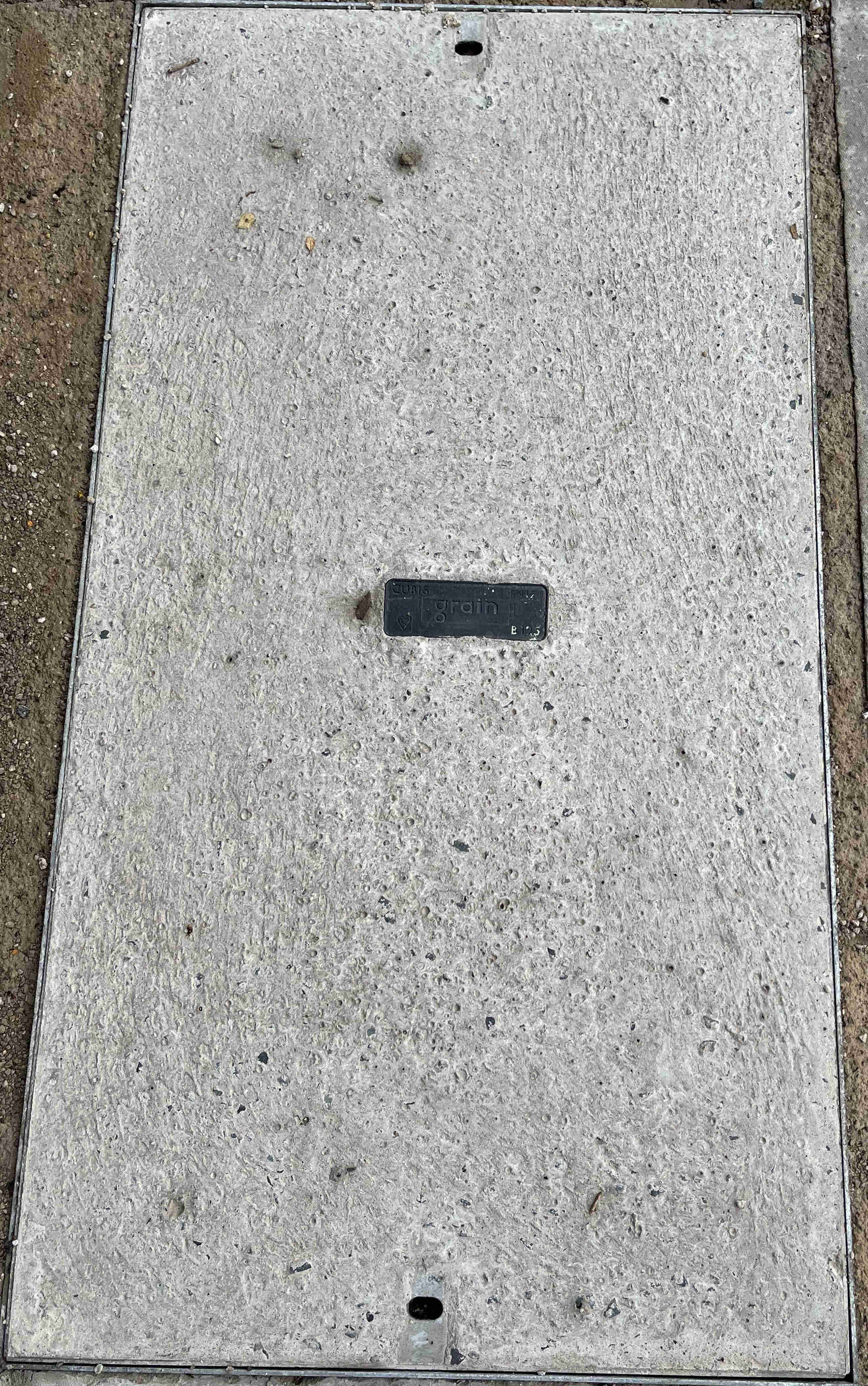
Grain
Grain, also known as Grain Connect, are an AltNet building FTTP access networks across the UK:
InternetTY.
InternetTY. (Internet ThankYou) are an AltNet in building FTTP access networks in rural and semi-urbanised areas across the UK:
Interoute.
Interoute was founded in 1995 and in 2014 acquired VTESSE:
Jersey Telecom
A state monopoly was formed in 1973 and operated the telecoms network on the island (called Jersey Telecom) exclusively until 2003 when the market was opened to competition. In 2003 Jersey Telecom become a private company 100% owned by the States of Jersey. In September 2011, Jersey Telecom changed its name to JT. JT also operate on Guernsey.
Photo provided by Ollie King.
KCOM / Kingston
Kingston Communications Ltd. Kingston were originally the sole provider of Telecoms infrastructure in the Hull and East Riding area (BT Openreach have since started to provide services in this area). In 1922 Kingston services went live as the only remaining municipally owned telephone corporation that wasn't merged into the nation incumbent BT. In 1994 Torch Telecom was launched as a joint venture between Yorkshire Electricity and Kingston Communications. In 1996 Kingston bought out Yorkshire Electricity's share of Torch Telecom, making it a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Kingston Group. Kingston later rebranded to KCOM in 2007. From 2009, the management of some of its network assets have been outsourced to BT Group plc. In 2015 KCOM sold it's network assets to CityFibre.
Gobal Crossing / Level3 / CenturyLink
Global Crossing. Global Crossing was formed in 1997. In July 1999 Global Crossing acquired Global Marine Systems from Cable & Wireless. In September 1999 Global Crossing acquired Frontier Communications (formerly Rochester Telephone Corporation) and renamed it Global Crossing North America. In September 1999 Global Crossing formed a joint venture called Asia Global Crossing. Asia Global Crossing was sold in November 2002 to Asia Netcom, a subsidiary of China Netcom. In November 1999 Global Crossing acquired Racal Telecom. GC PEC was Global Crossing's Pan European Crossing brand (GC PEC UK picture provided by Tom Brook).
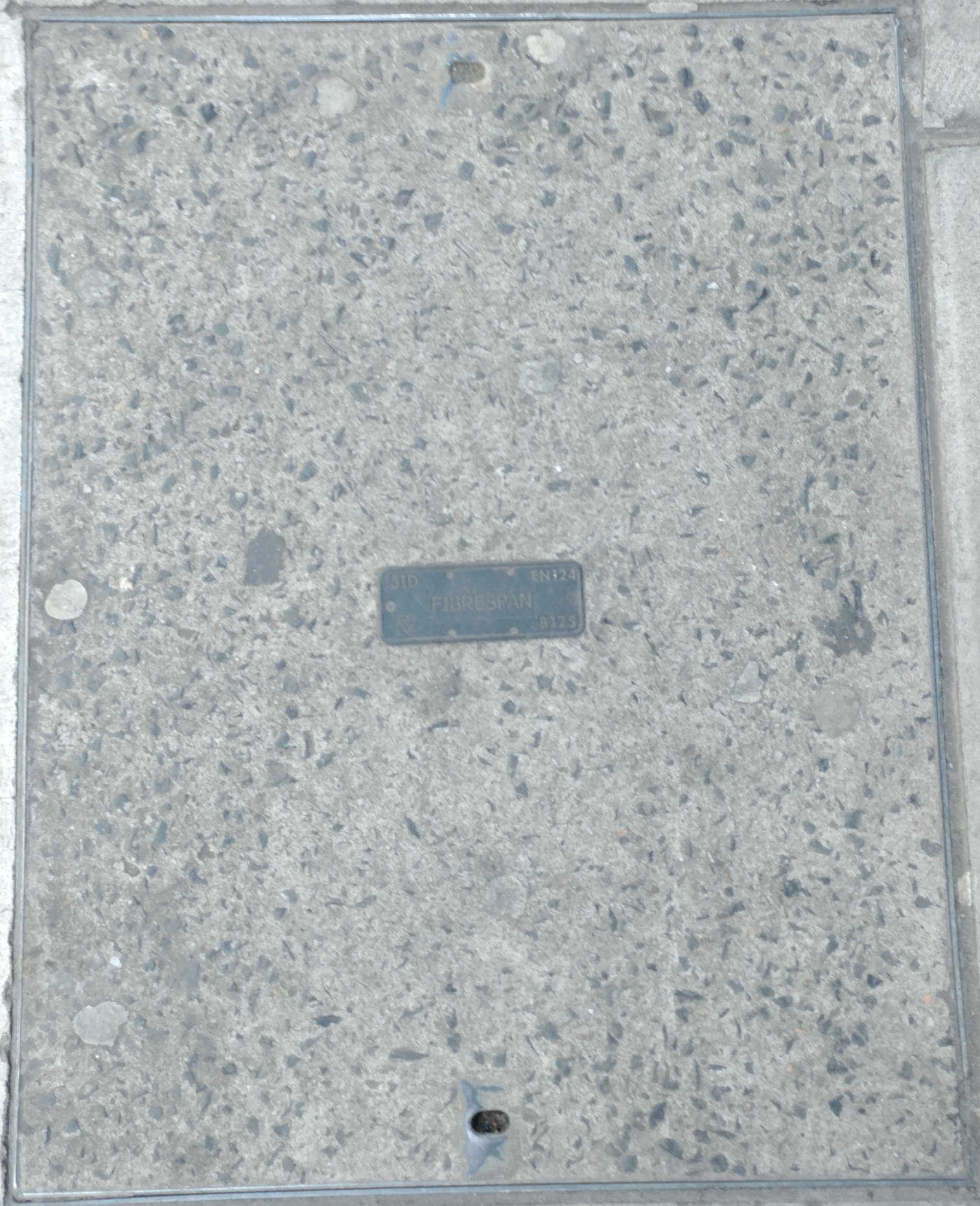
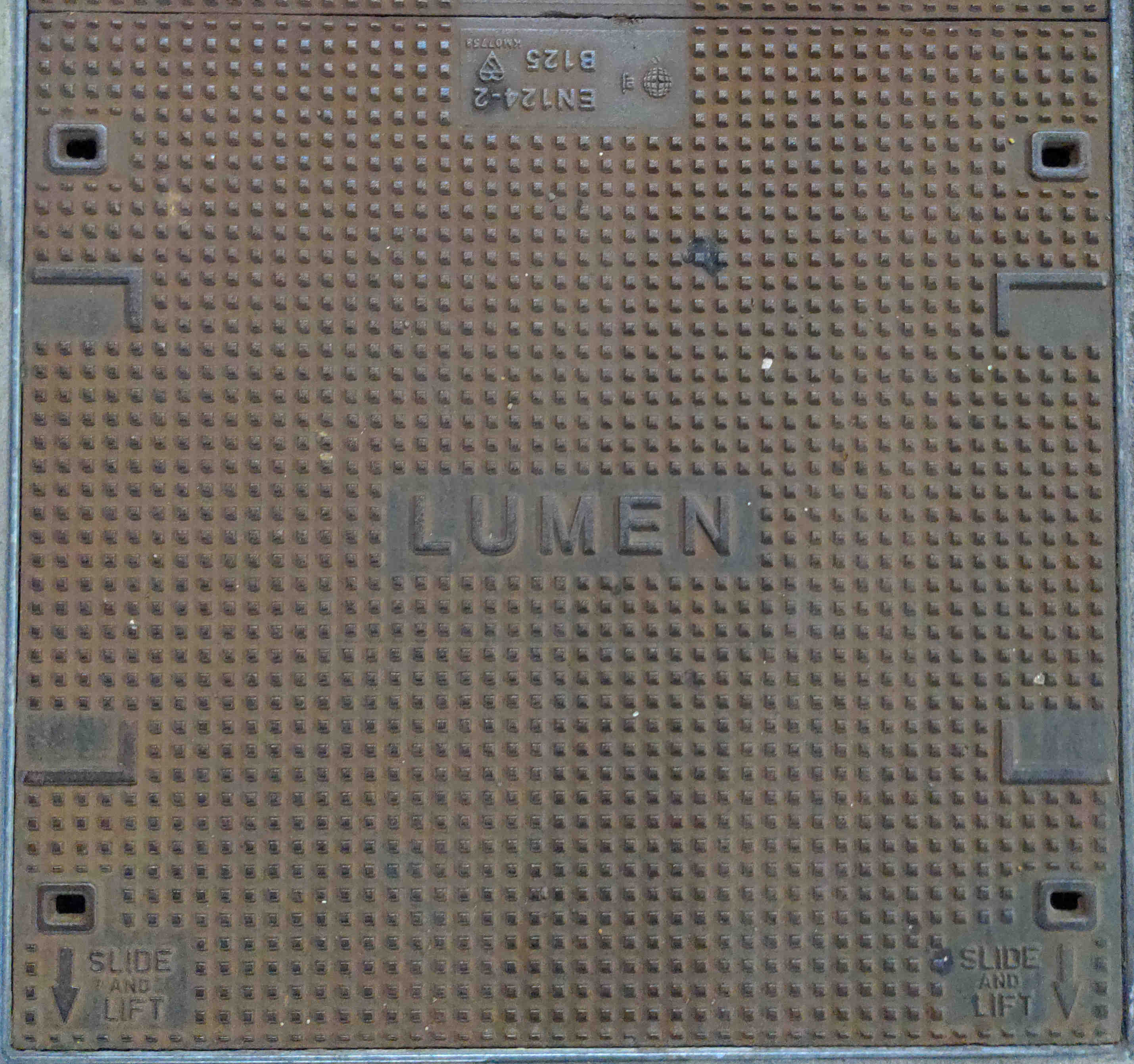
Level 3 Communications. Level 3 was formed in 1998 when it was spun out of a parent company, and went on to become a Tier 1 IP transit provider. In October 2011 Level 3 purchased Global Crossing which was another Tier 1 transit provider. Level 3 purchased Fibrespan in August 2012. In 2014 Level 3 purchased Time Warner Communications (a.k.a TW Telecom). Level3 was purchased itself by CenturyLink in 2017 and rebranded as CenturyLink.In 2020 CenturyLink rebranded as Lumen
In 2023 Lumen was bought by Colt:
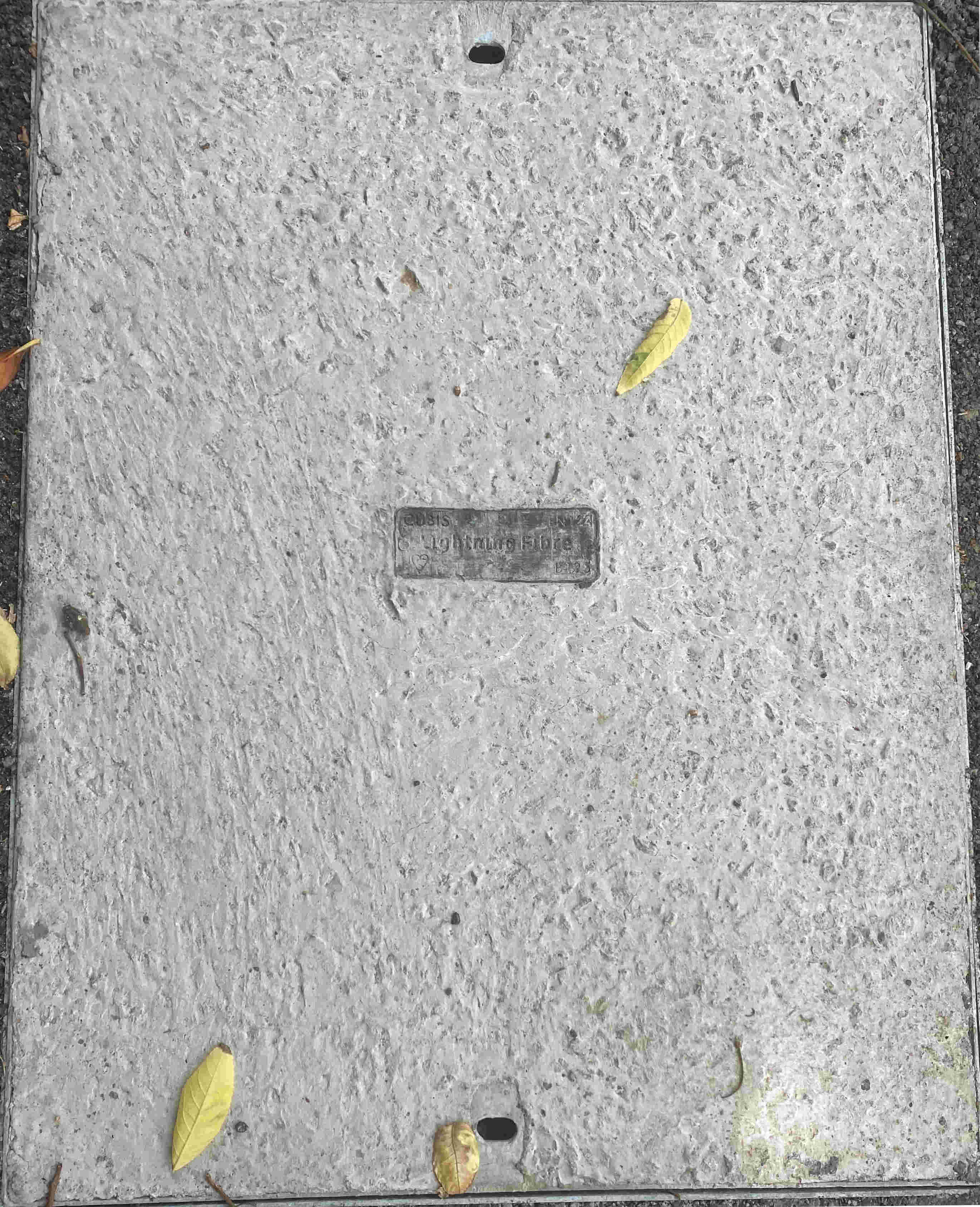
Lightning Fibre
Ligthning Fibre started in 2018. They are an FTTH/FTTP builder who initially focused on the south east of England.
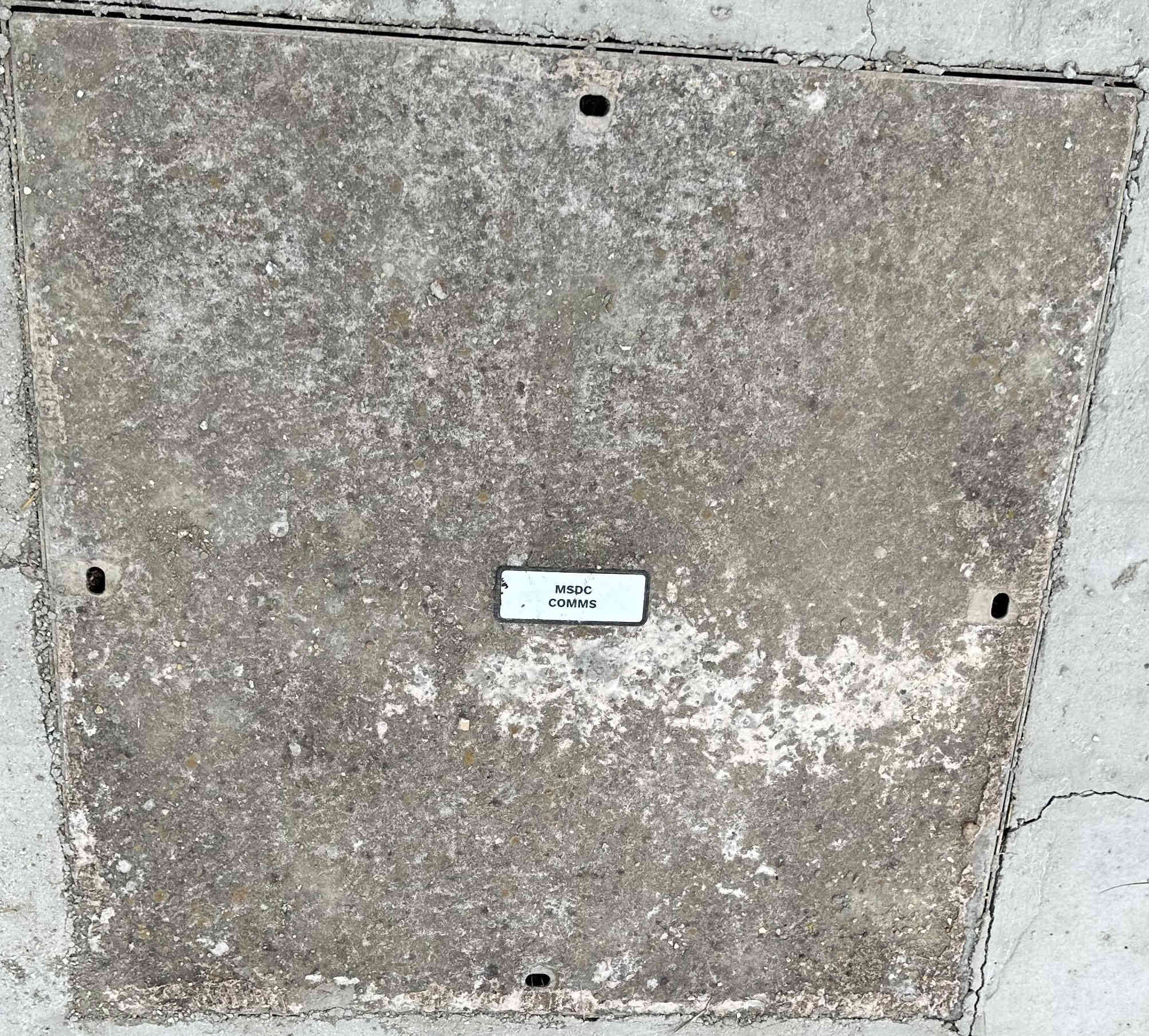
Mid Sussex Distric Council
They have their owd dark fibre network. Photo from Matt Iggo.
Netomnia
Netomnia started in 2019. They are an FTTH/FTTP builder, laying fibre in various regions across the UK.
Next Gen Access
"NextGenAccess", also known as NGA, were a wholesale FTTP network builder, building out across the UK.
In September 2022 NGA were bought by ITS. ITS are an existing owner of multiple wholesale FTTP networks across the UK.
Norweb plc, originally the North Western Electricity Board launched a telecommunications division in 1994 called Norweb Communications Ltd which used their existing utilities infrastructure to provide copper and fibre connectivity (amongst other services). North West Water acquired Norweb in 1995. In 1996 the company renamed to United Utilities Plc but kept the Norweb branding until 2001. At some point Norweb Communications Ltd renamed to Norweb
Telecom Limited. In May 2001 Norweb Teelcom rebranded to Your Communications due to United Utilities wanting to get all it's connectivity, voice, and data services under a single brand. Around mid 2005 Your Communications has 3600 kilometres of fibre in the UK. In 2006 the network was sold to Thus under the name Your Communications. Thus was later taken over by C&W and that was later taken over by Vodafone.
CATV / Cable Television / NTL (National Transcommunications Ltd) / VM (VirginMedia):
NTL / "ntl:" and Telewest were both cable TV providers in the UK.
International CableTel was established in 1993. In 1996 CableTel purchased NTL and rebranded as "NTL". Earlier Telecential had formed, a regional CATV operator in Hertfordshire. Telecential were later bought by Comtel, and included in the CableTel to NTL rebrand.
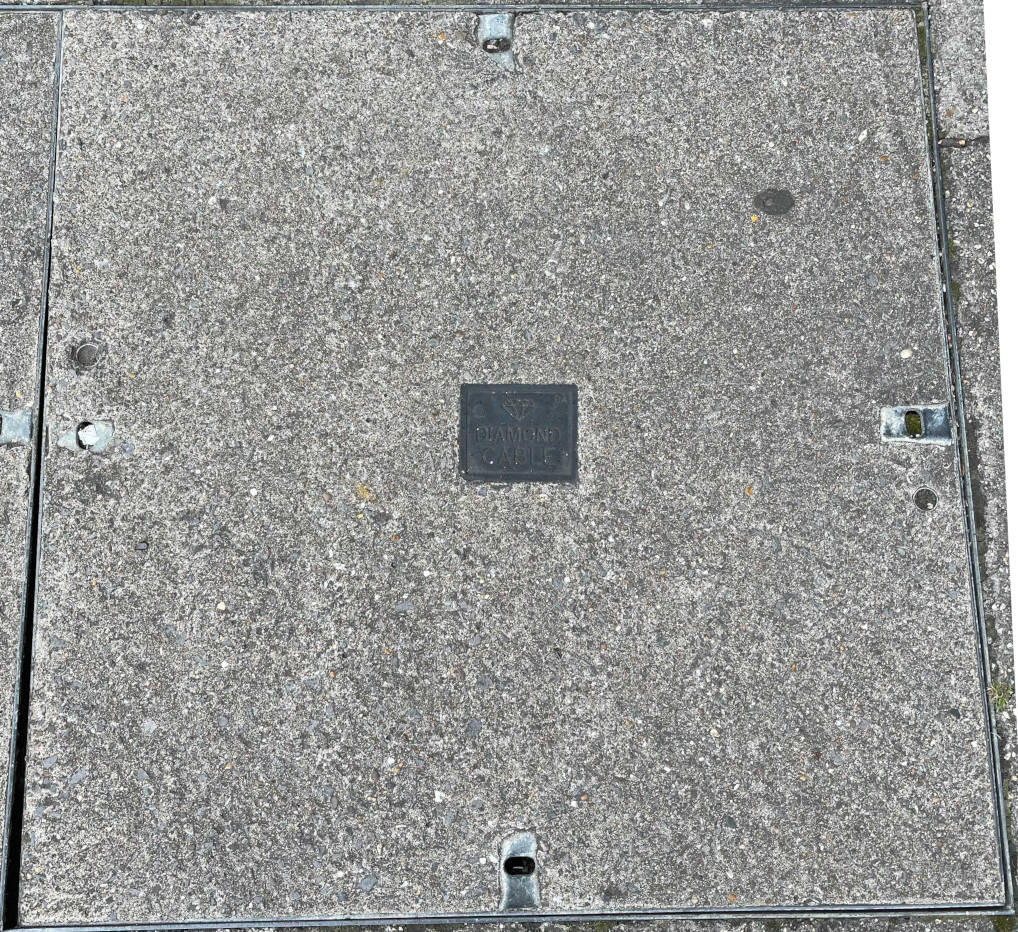
Diamond Cable Communications Limited started in August 1994, laying their own telephones lines and building their own telephone exchanges, to be independant from BT. They provided telephone services and TV over twister copper pairs, as well as cable TV services, in the East Midlands and had a coverage of 1.2m homes. In 1998 NTL purchased Diamond.
Meanwhile, Telewest began in 1984 in Croydon under the name "Croydon Cable". The company expanded during the 1990s and adopted the "Telewest" name in 1992. It expanded into cable television access in 1999 by purchasing the remaining 50% stake in "Cable London", one of the first cable TV companies in the UK, from NTL.
ComTel were another cable network operator, which covered the Midlands and South East regions with reach of 1.1m homes. NTL acquired ComTel in 1998.
Eastern Group Telecoms were another cable network operator (a subsidiary of Eastern Electricity, although the telecoms network seems to have extended beyond the scope of the electrical network), which covered East Anglia and Kent (maybe more?). NTL purchased Eastern Group Telecoms network assets in 1998 (EGT photo below provided by Tom Brook, info from Dan Glover - thanks!).
NTL purchased Cable and Wireless' cable operations in 1999.
In 2005 NTL merged with Telewest (formerly Telewest Broadband and Telewest Communications, a triple play cable provider) and became the brand NTL:Telewest a.k.a NTL Incorporated. NTL:Telewest was later merged with Virgin Media (after buying Virgin.net ISP in 2004).
Virgin Media was later bought by Liberty Global.
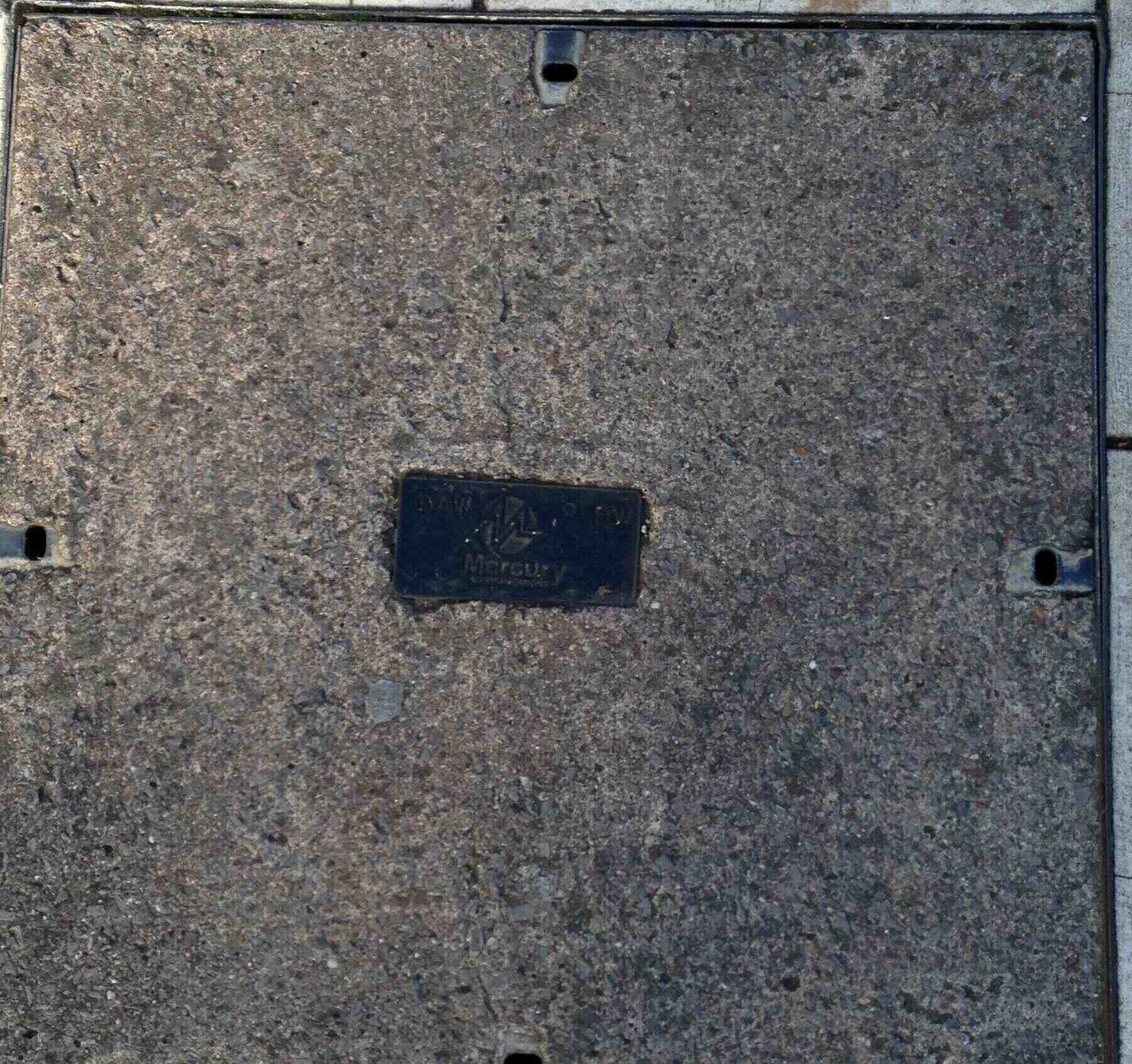
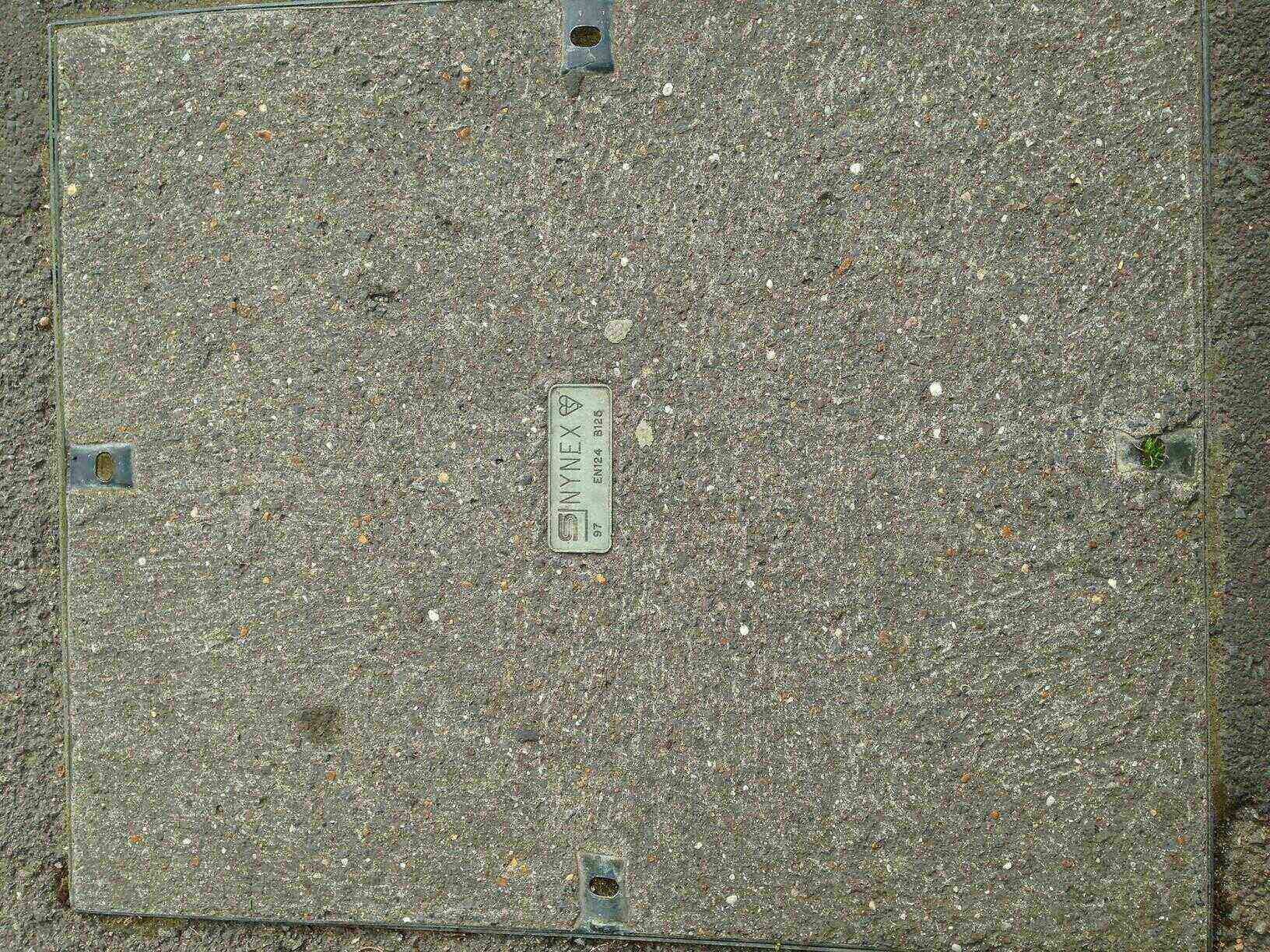
NYNEX UK division which provided cable TV. UK assets of NYNEX were merged with the Cable & Wireless subsidiary Mercury Communications, and renamed as Cable & Wireless Communications. Cable & Wireless's cable assets were sold to NTL in 1999-2000:
Oxford University Telecoms Network.
Within the city of Oxford, the university runs it's own telecoms network:
Portsmouth
Like many universities, Portsmouth runs it's own network within the city.
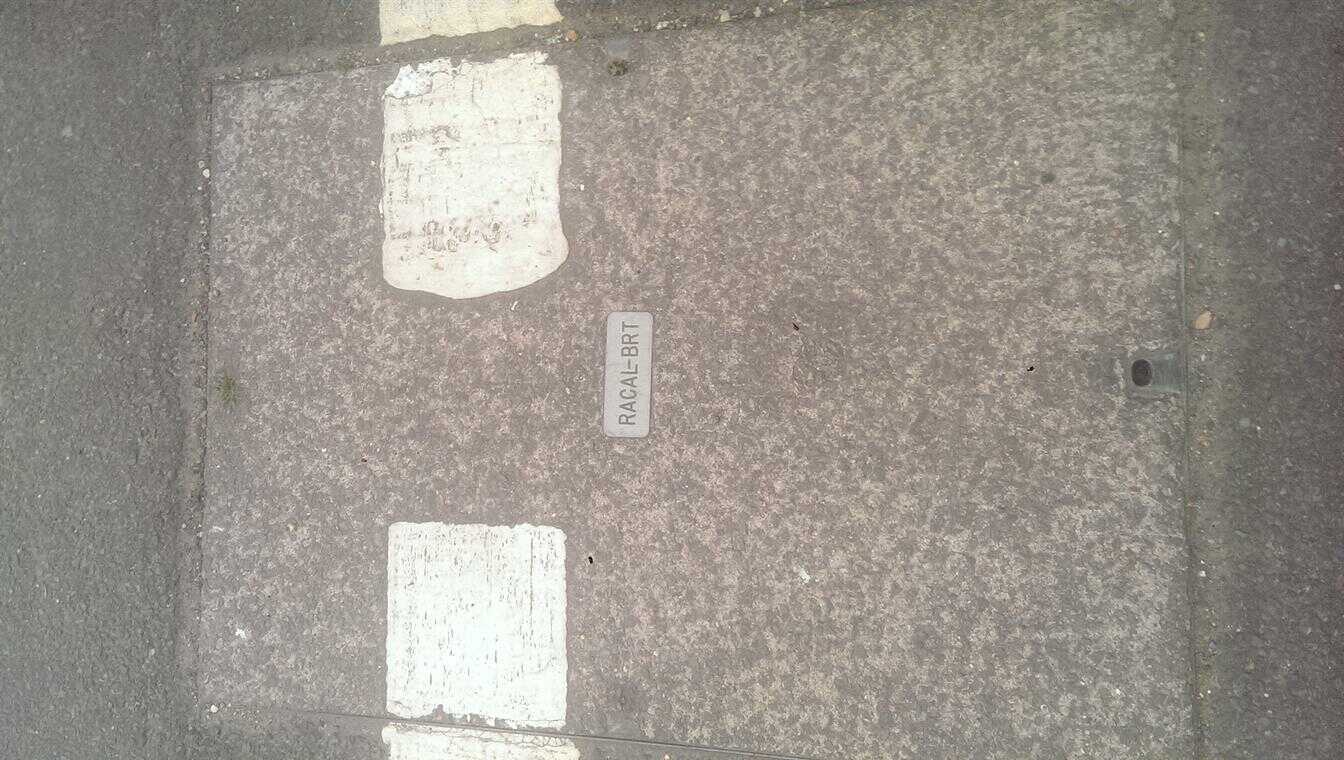
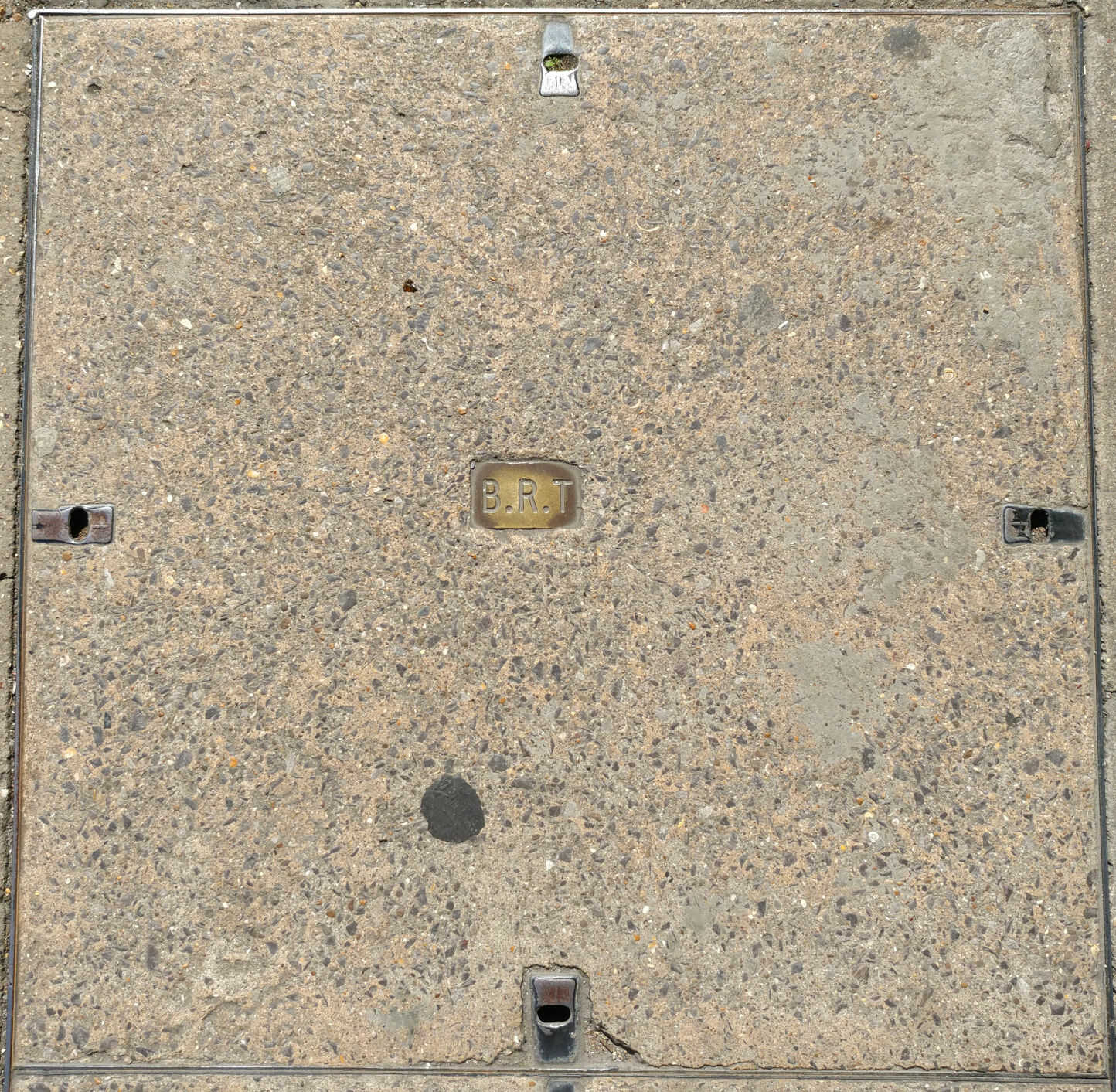
BRT / Racal Electronics plc / RACAL.
British Rail Telecommunications was created in 1992 by British Rail (BR). BRT was later bought by Racal Electronics in 1995 and became Racal-BRT. RACAL-BRT merged with Racal Network Services (RNS) to become Racal Telecom. RACAL eventually sold its telecoms business to Global Crossing. (Global Crossing was bought by Level3, Level3 was later bought by CenturyLink, and CenturyLink later rebranded to Lumen Technologies). This means that the present day version of RACAL owns a lot of rail-side fibre in the UK:
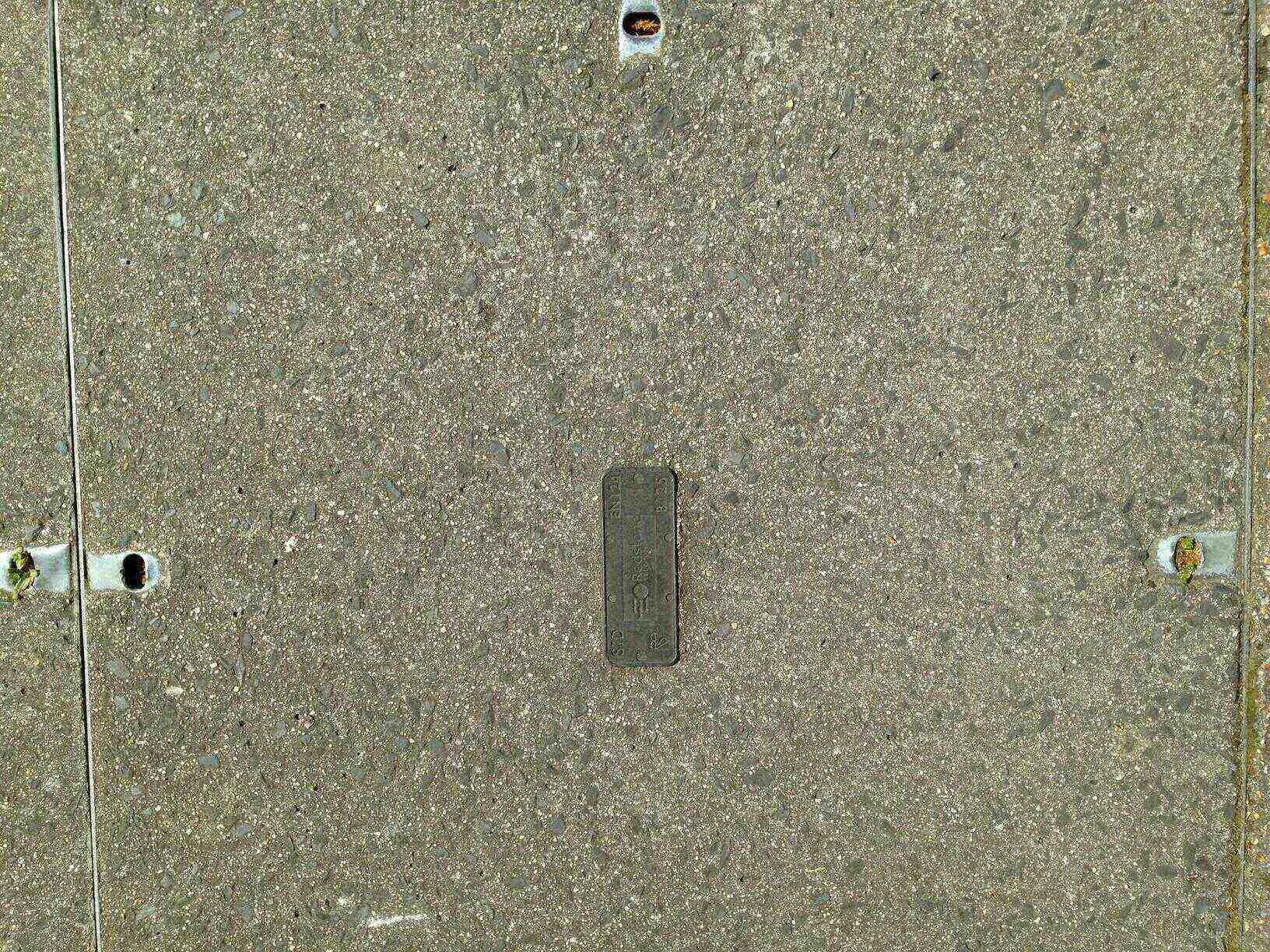
Redstone Telecom.
Redstone previously purchased Symphony Telecom:
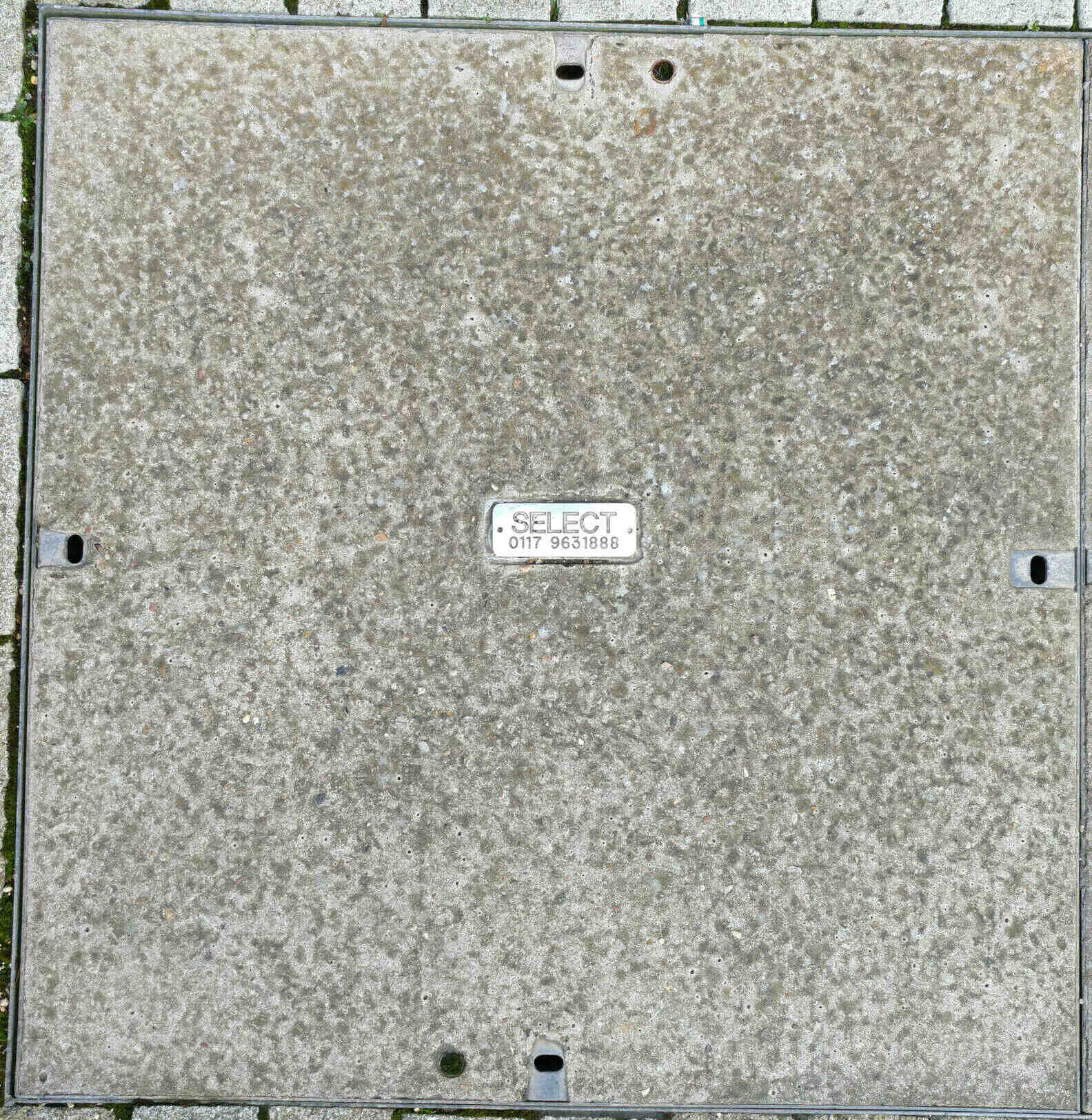
Select (Bristol):
Select Electrics Limited was established in 1997. Originally an electrical installation and maintenance specialist, Select expanded to become a leading provider of CCTV systems installation and maintenance with expertise in telecommunications and fibre optics networks.
A fibre optic network system has been installed [around Bristol] by Select Electrics which manages over 1000+ cameras located throughout the city and many surrounding towns, public area and businesses nearby.
Presumably this is related to BNET near the top of this page?
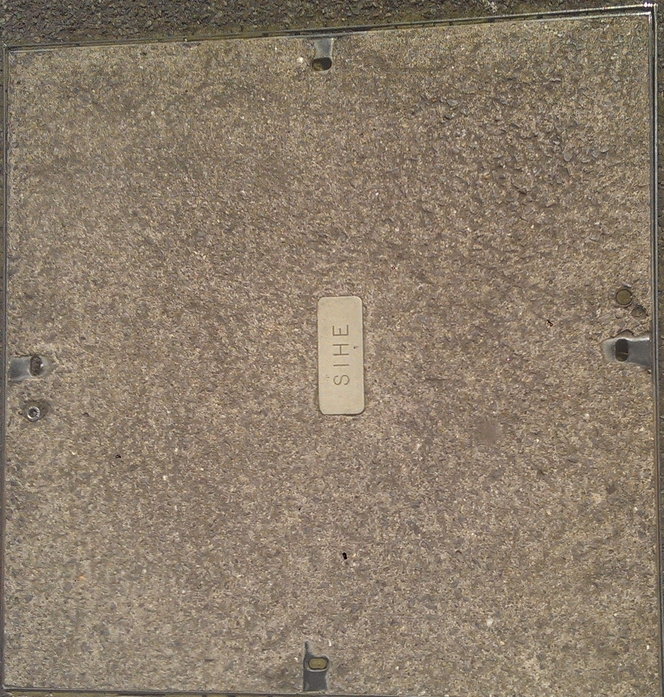
Various colleges banded together to form Southampton Institute of Higher Education. Later the institutes became a university called Southampton Solent University which later changed name to Solent University. Due to the distributed nature of the university buildings around the city their own communications infrastructure was laid. It was also common for companies like the BBC to share ducts or infrastructure with such institutes:
Sky / BSkyB / EasyNet
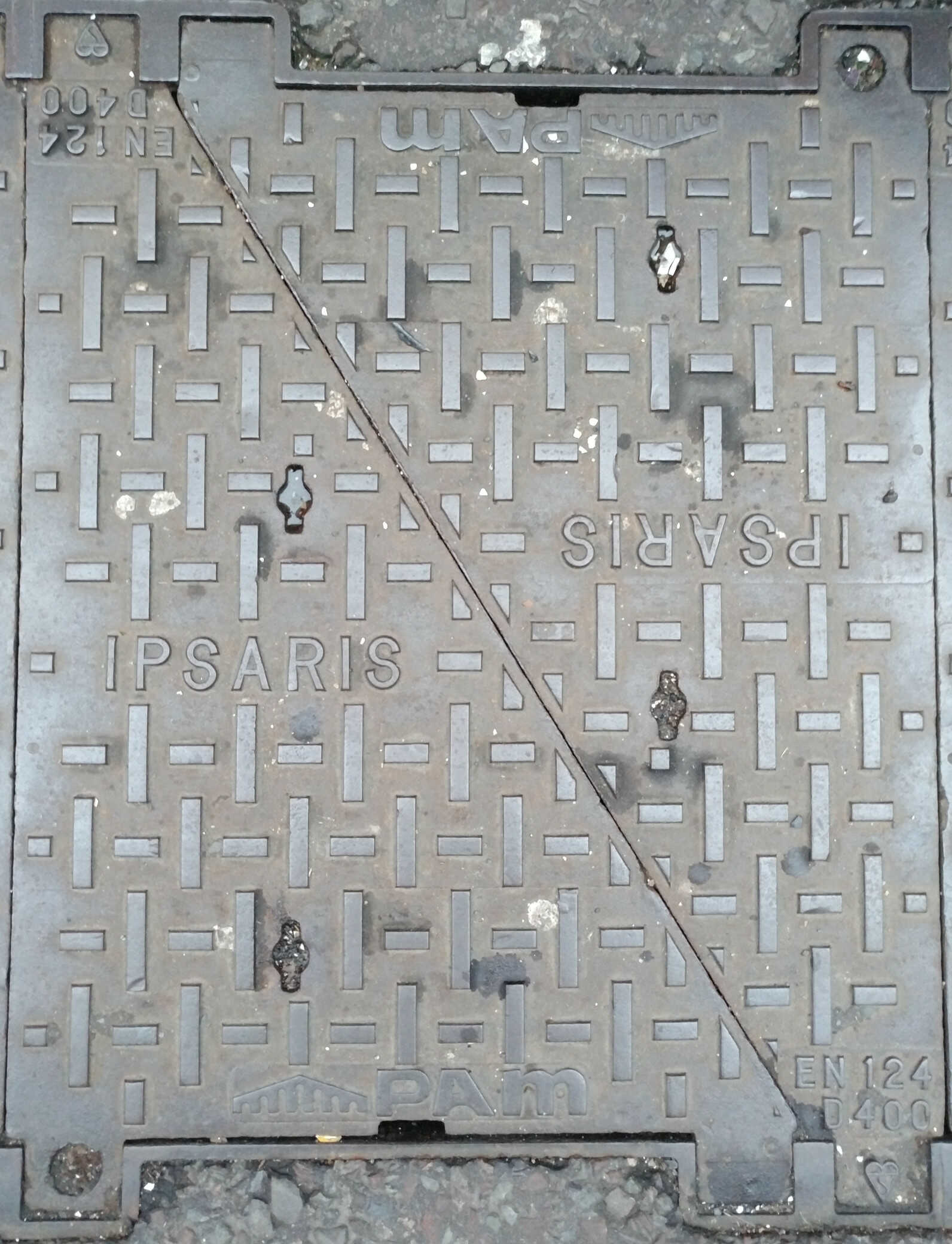
Sky (originally British Sky Broadcasting Limited a.k.a BSkyB) was formed by a merger of Sky Television and British Satellite Broadcasting in 1990. Separately, in 1994 the managed ISP Easynet was formed. In 1994 Ipsaris (which was owned by General Electric Company) and state-owned British Waterways formed a joint venture call Fibreway, which laid 3,500km of ducting along canal towpaths nationwide in the UK. A figure-of-eight DWDM and SDH network was built. In 2001 Easynet bought the fibre provider Ipsaris. Later in 2005 Sky bought the LLU and managed service provider Easynet (which included the Fibreway/Ipsaris fibre estate) and merged most of it into the Sky network. In 2010 Sky sold what was left of Easynet estate and contracts to investment firms and in 2015 that version of Easynet was sold again, this time to Interoute. In 2013 Sky also bought the o2 and BE LLU footprint from Telefonica UK. In 2019 Sky bought the SeeTheLight FTTP retail provider:
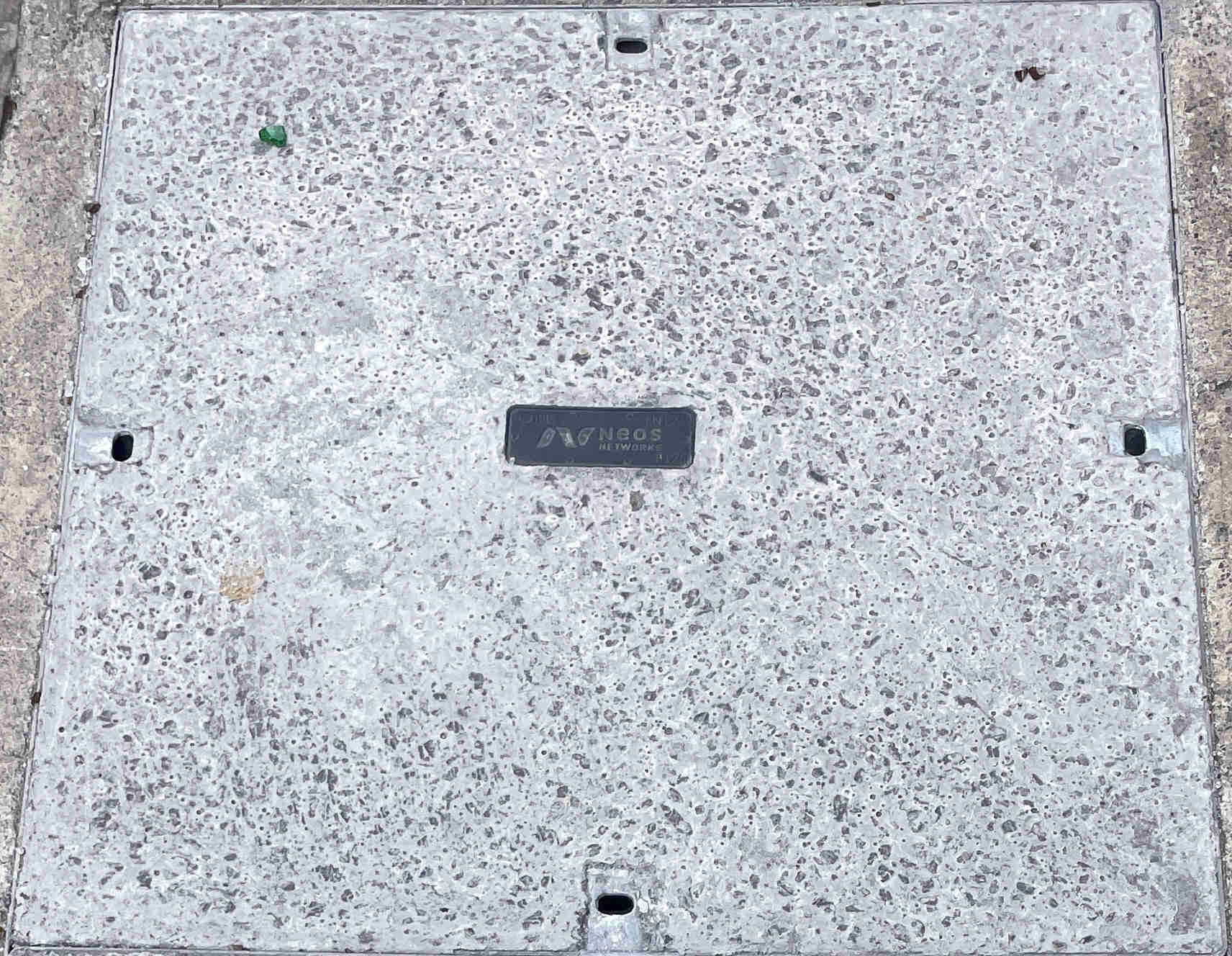
SSE
SSE (Scottish and Southern Energy) build power networks across the UK and run fibre over their pylon network. The network division of SSE is called SSEET (SSE Enterprise Telecoms).
In 2021 SSEET rebranded to NEOS Networks.
SWEB Telecom / SURF Telecom / WPD Telecom / National Grid Telecoms
SWEB Energy (South Western Electricity Board) were formed in 1990 (when SWEB Energy, which was state owned, was privatised).
Somewhere around 1995 SWEB Telecom is born.
In 1999 WPD Telecoms (Western Power Distribution) buys SWEB Telecoms and re-brands it as Surf Telecom. WPD Telecoms is owned by PPL Corporation (Pennsylvania Power & Light).
In 2018 or 2019 ? Surf Telecom is re-branded to WPD Telecom.
In 2021 WPD Telecoms was exchanged as part of a deal with between it’s then parent company, PPL Corporation, and new owner, National Grid. WPD Telecoms was re-branded to National Grid Telecoms and in 2022 it’s parent re-branded from National Grid to to NGED (National Grid Electricity Distribution).
Today National Grid Telecoms are a small independent fibre company that operates in East and West Midlands, South West and Wales. They carry their own data and that of National Grid Electricity Distribution, and lease dark fibre to other companies. Some fibre is carried overhead on pylons and others run through their own duct network.
(Credit to Thomas Stone for these!)
Swish Fibre
Swish are an FTTP/FTTH AltNet in the UK which started in 2019.
In 2019 People’s Fibre was founded and they started to build and operator their own FTTH network. In 2021 Swish Fibre acquired People’s Fibre.
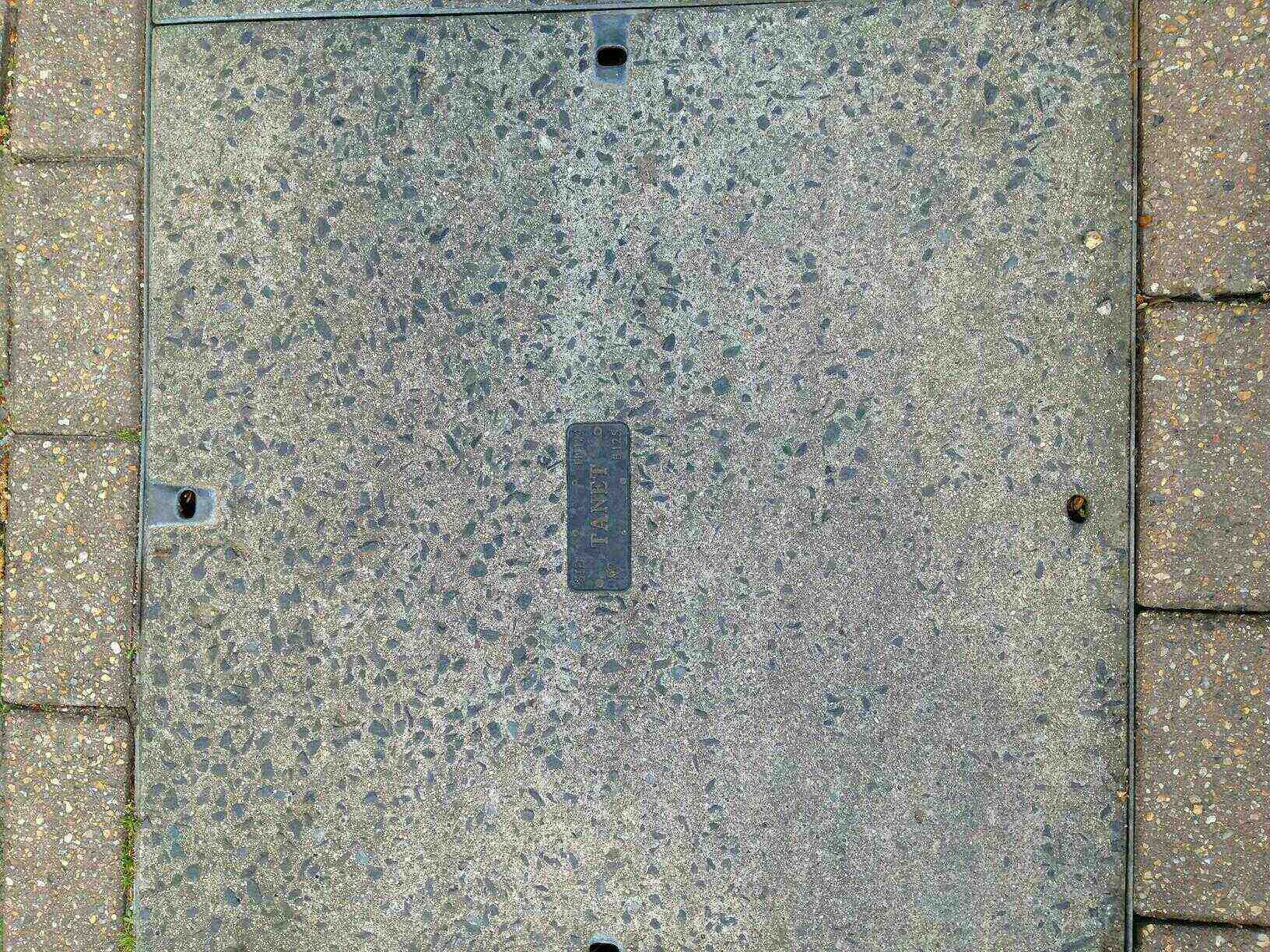
TANet was built using leased rail-side fibre from Racal Telecom to create a national SDH network. TANet was owned by Fibernet. Fibrenet was later acquired by Global Crossing. Companies like Merlin Communications and EasyNet leased capacity from TANet with EasyNet later being acquired by BSkyB:
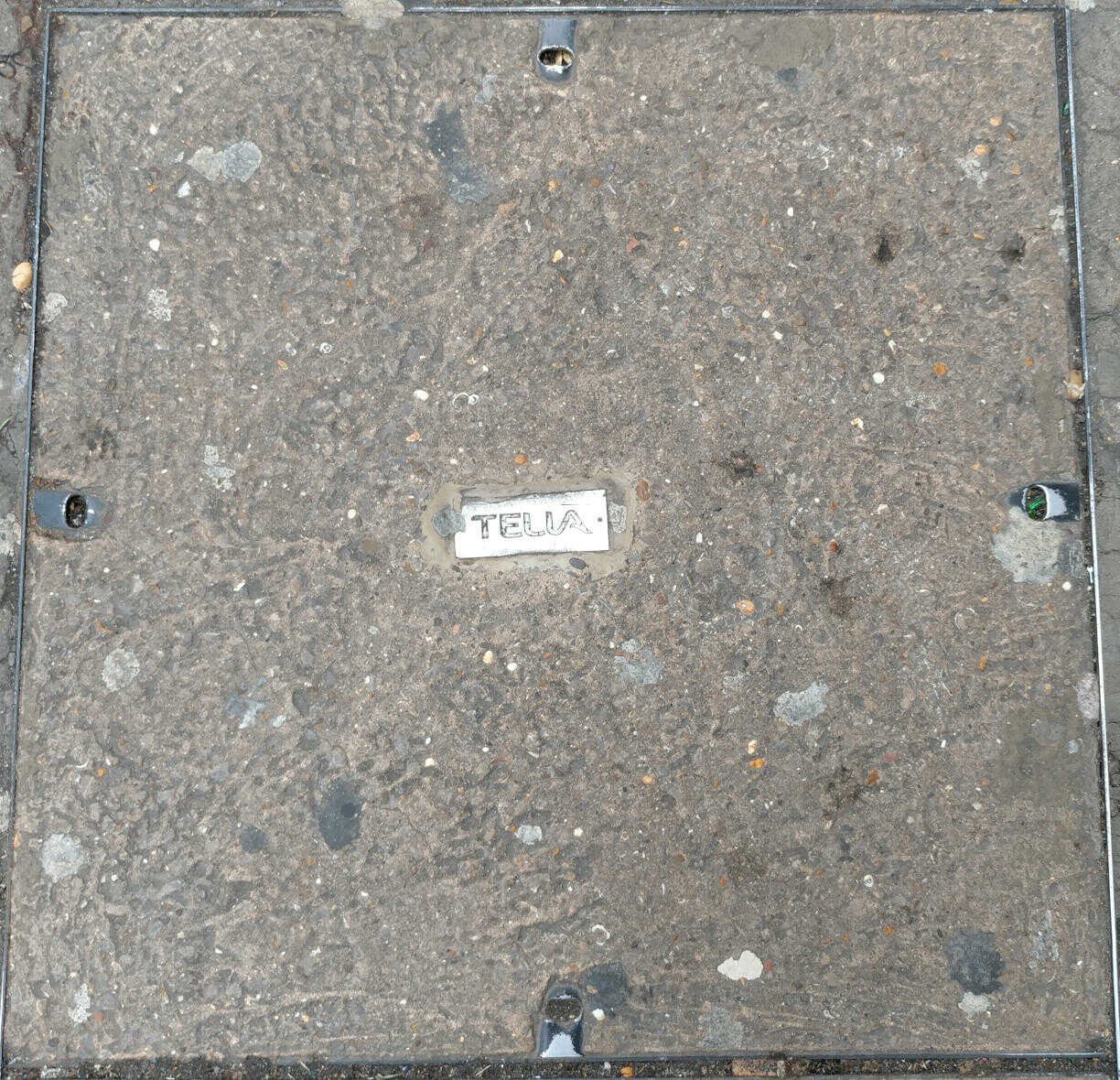
Telia was the original state provider in Sweden which was later devided and privatised. Sonera was the national Finish provider. The Swedish and Finish companies merged in 2002 to form TeliaSonera:
TfL / BAI
TfL (Transport for London) are the company responsible for transport within London (buses, tubes, roads etc.). Like many utility providers, TfL have run a lot of fibre around London whilst performing construction and maintenance work and now have their own communications infrastructure around the capital.
The National Transmission Agency (NTA) was established in July 1992 by the Australian government to supervise the operation of the National Transmission Network (NTN). The NTN was, and still is, the network of radio and television transmitters that broadcast the programs of Australia's national broadcasters. The government chose to privatise the NTA in 1997. Macquarie Bank acquired NTA in 2002 - the seed asset in Macquarie Communications Infrastructure Group (MCIG), and rebranded it as Broadcast Australia. MCIG, including Broadcast Australia, was acquired by the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board in 2009. In November 2019, Broadcast Australia was rebranded BAI Communications. In June 2023, BAI rebranded their business in the northern hemisphere to Boldyn Networks (the BAI name was retained in Australia and remain under the ownership of the Canada Pension Plan Investment Board). This was due to the combining of six businesses in Europe and North America (as well as the European and North American businesses of BAI itself; ZenFi which owns fiber across New York; Mobiliti which owns antenna networks, small cells, and tower sites across the US; Signal Point Systems which has small cells on US military bases; Transit Wireless which operates the Transit Wireless New York City subway network; Vilicom in Ireland and the UK which specializes in 4G and 5G). BAI secured a 20-year concession in UK from Transport for London (TfL) to provide neutral host mobile connectivity for the London Underground. In October 2021 Sunderland city council awarded BAI a 20-year deal to design, build and operate infrastructure including a private 5G small cell network.
Thus. Originally founded in 1994 as Scottish Power Telecommunications Holdings Ltd (trading as Scottish Telecom), an offshoot of the energy company Scottish Power. In 1998 the company acquired Demon Internet. In 2002 it was demerged from Scottish Power under the name Thus. On 30 June 2008, Cable & Wireless announced that it had acquired a 29.9% stake in Thus. On 1 October 2008, Cable & Wireless completed the takeover of Thus.
TyCom
In 1997 Tyco International Ltf acquired AT&T Submarine Systems. Combined with Tyco Integrated Cables Systems, Tyco Telecommunications was established. Under the TyCom brand, Tyco International Ltd build a global undersea fiber-optic network known as Tyco Global Network (TGN) which was completed in 2003. In 2005 Videsh Sanchar Nigam Limited (VSNL) acquired the TGN from Tyco International. VSNL was completely acquired by the Tata Group in 2002 and renamed Tata Communications in 2008.
Verizon
Verizon (a.k.a Verizon Communications) was born out of a division of AT&T Corporation in the US into 7 US regional operators. In 1996 UUNET was purchased MFS Communications (Metropolitan Fiber Systems Inc) and four months later still in 1996 MFS was purchased by WorldCom. In 2006 Verizon Communications purchased WorldCom (which it merged into it's Verizon Business brand). In 2015 Verizon purchased AOL and in 2017 Verizon purchased Yahoo!:
Vodafone
Originally formed as Racal-Vodafone (Holdings) Ltd and eventually spun out of Racal Telecoms to become Vodafone. Vodafone has since purchased Cable and Wireless and Kabel Deutschland (now VKD / Vodafone Kabel Deutschland):
Vorboss
Vorboss formed in 2006. Vorboss had a focus on building FTTP in dense metropolitan areas, starting with London. Feb 2021 - Vorboss is acquired by Fern Trading Limited / Fern Fibre Limited. At this time, Fern also own majority stakes in Jurassic Fibre and Swish Fibre.
Your Communications
? Seen in Manchester
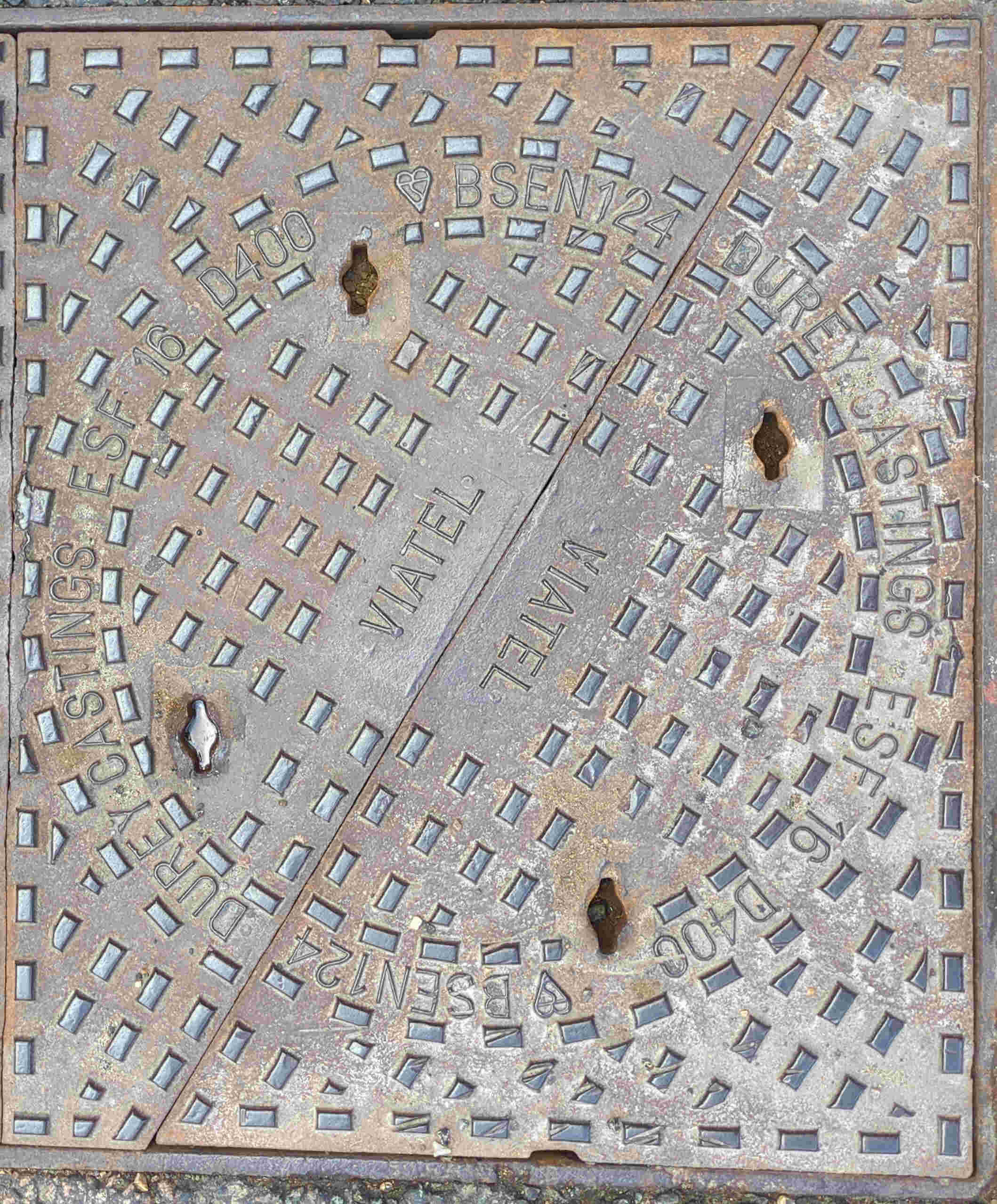
186k / AboveNet / Geo / MetroMedia / Viatel / Zayo.
Viatel was founded in the USA in 1991. Viatel built and operated fibre networks across the USA and Europe.
186K formed in the early 1990s?, and were a reseller ISP based in Leeds who built their own core fibre network in Leeds and London.
Lattice Group was established in 2000 when BG Group demerged its UK gas transmission business, formerly known as Transco, and named it Lattice Group. Lattice Group had been building the gas network in the UK and laying fibre along the gas lines. In October 2002 National Grid Group merged with Lattice Group, and renamed to National Grid Transco.
186K was purchased from National Grid Transco by Hutchinson Geo in December 2002. Hutchinson later sold Geo Networks to Zayo Group in 2014.
Meanwhile: In 1993 National Fiber Network was formed in the US which provided fibre in the US and Europe. In 1997 National Fibre Network changes it's name to Metromedia Fiber Network. In 1999 Metromedia acquired Abovenet Communications. In 2002 the company filed bankruptcy and in 2003 the company emerged from bankruptcy as Abovenet.
In 2012 Zayo Group acquired Abovenet.
In 2015 Zayo acquired Viatel's UK and European network assets.
Previous page: Netra T1 105 LOM Serial Cable
Next page: .Call Files Intro