Date created: Saturday, January 11, 2014 2:44:51 PM. Last modified: Wednesday, September 27, 2017 3:44:01 PM
VRF & L3VPN Packet Leaking
Example 1: Packet leaking from VRF to GRT
CE for AS50 is inside VPN VRF Cust 1, PE for AS100 has static default global route inside VRF to allow break out to Internet and static route in global using next hop interface to route back into the VRF for returning Internet traffic (PE router for AS200's loopback represents "The Internet");
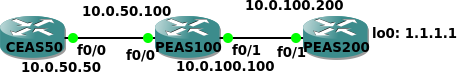
CEAS500
interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.50.50 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.50.100
PEAS100
ip vrf Cust1 rd 100:1 ! interface FastEthernet0/0 ip vrf forwarding Cust1 ip address 10.0.50.100 255.255.255.0 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 10.0.100.100 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.0.100.200 ip route 10.0.50.0 255.255.255.0 FastEthernet0/0
! The interface specification here allows traffic back into the VRF ! ip route vrf Cust1 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.100.200 global
! The global keyword here allows leaking from within the VRF to the default PE table,
! which contains full Internet routing
PEAS200
interface Loopback0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 ! interface FastEthernet0/1 ip address 10.0.100.200 255.255.255.0 ! ip route 10.0.50.0 255.255.255.0 10.0.100.100 ! PEAS100 would redistribute this subnet ! into BGP For global routing access
Example 2: Packet leaking between two L3 VPNs
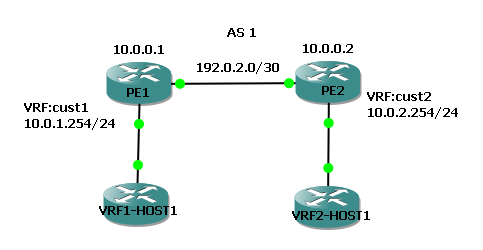
PE1 is leaking a route into the cust1 VRF for the customer 2 host (10.0.2.1/32) via a next hop in it's Global Routing Table, that points to PE2's GRT loopback0 address. PE2 is leaking a route into the cust2 VRF that routes to the customer 1 host (10.0.1.1/32) via a next hop in it's GRT, that points to PE1's GRT loopback0.
For the return routes, PE1 has a route in it's GRT that points to the customer 1 host (10.0.1.1/32) via the interface the customer 1 host is connected to (fa0/0, because that interface is inside the VRF cust1). Vice verse, PE2 has a route in it's GRT that points to the customer 2 host (10.0.2.1/32) via the interface the customer 2 host is connected to (fa0/0, because the interface is inside the VRF cust2).
hostname VRF1-HOST1 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 exit ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.1.254
hostname PE1 ip vrf cust1 rd 10.0.0.1:100 route-target export 65001:100 route-target import 65001:100 exit ip vrf cust2 rd 10.0.0.1:200 route-target export 65002:100 route-target import 65002:100 exit interface Loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255 exit interface FastEthernet0/0 description Link to VRF1-HOST1 ip vrf forwarding cust1 ip address 10.0.1.254 255.255.255.0 exit interface FastEthernet0/1 description Link to PE2 ip address 192.0.2.1 255.255.255.252 ip ospf 1 area 0 mpls ip exit router ospf 1 router-id 10.0.0.1 passive-interface default no passive-interface FastEthernet0/1 network 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.0 area 0 exit router bgp 1 bgp router-id 10.0.0.1 neighbor 10.0.0.2 remote-as 1 neighbor 10.0.0.2 update-source Loopback0 address-family ipv4 no neighbor 10.0.0.2 activate exit-address-family address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.0.0.2 activate neighbor 10.0.0.2 send-community extended neighbor 10.0.0.2 next-hop-self exit-address-family address-family ipv4 vrf cust1 redistribute connected exit-address-family exit ip route 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0 ip route vrf cust1 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.255 10.0.0.2 global
hostname PE2 ip vrf cust1 rd 10.0.0.2:100 route-target export 65001:100 route-target import 65001:100 exit ip vrf cust2 rd 10.0.0.2:200 route-target export 65002:100 route-target import 65002:100 exit interface Loopback0 ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.255 exit interface FastEthernet0/0 description Link to VRF2-HOST1 ip vrf forwarding cust2 ip address 10.0.2.254 255.255.255.0 exit interface FastEthernet0/1 description Link to PE1 ip address 192.0.2.2 255.255.255.252 ip ospf 1 area 0 mpls ip exit router ospf 1 router-id 10.0.0.2 passive-interface default no passive-interface FastEthernet0/1 network 10.0.0.2 0.0.0.0 area 0 exit router bgp 1 bgp router-id 10.0.0.2 neighbor 10.0.0.1 remote-as 1 neighbor 10.0.0.1 update-source Loopback0 address-family ipv4 no neighbor 10.0.0.1 activate exit-address-family address-family vpnv4 neighbor 10.0.0.1 activate neighbor 10.0.0.1 send-community extended neighbor 10.0.0.1 next-hop-self exit-address-family address-family ipv4 vrf cust2 redistribute connected exit-address-family exit ip route 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.255 FastEthernet0/0 ip route vrf cust2 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.255 10.0.0.1 global
hostname VRF2-HOST1 interface FastEthernet0/0 ip address 10.0.2.1 255.255.255.0 ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.0.2.254
PE1#show ip route | b 10
10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 3 subnets
C 10.0.0.1 is directly connected, Loopback0
O 10.0.0.2 [110/2] via 192.0.2.2, 01:06:05, FastEthernet0/1
S 10.0.1.1 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
192.0.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.0.2.0/30 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
L 192.0.2.1/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
PE2#show ip route | b 10
10.0.0.0/32 is subnetted, 3 subnets
O 10.0.0.1 [110/2] via 192.0.2.1, 01:06:19, FastEthernet0/1
C 10.0.0.2 is directly connected, Loopback0
S 10.0.2.1 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
192.0.2.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.0.2.0/30 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
L 192.0.2.2/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1
PE1#show ip route vrf cust1 | b 10
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
C 10.0.1.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
L 10.0.1.254/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
S 10.0.2.1/32 [1/0] via 10.0.0.2
PE1#show ip route vrf cust2 | b 10
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 10.0.2.0 [200/0] via 10.0.0.2, 00:35:31
PE2#show ip route vrf cust1 | b 10
10.0.0.0/24 is subnetted, 1 subnets
B 10.0.1.0 [200/0] via 10.0.0.1, 00:35:43
PE2#show ip route vrf cust2 | b 10
10.0.0.0/8 is variably subnetted, 3 subnets, 2 masks
S 10.0.1.1/32 [1/0] via 10.0.0.1
C 10.0.2.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0
L 10.0.2.254/32 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/0 Previous page: VASI Inter-VPN Routing
Next page: VRF Basic Route Leaking